Введение
Когнитивные функции (КФ) представляют собой функции головного мозга, благодаря которым происходит процесс познания мира и взаимодействия с ним [1, 2]. В соответствии с этим выделяют следующие КФ: способность к восприятию информации (гнозис), память (сохранение и воспроизведение полученных данных), «исполнительные» функции (обобщение, переключаемость, формально-логические операции, создание ассоциативных связей, построение умозаключений), способность к целенаправленной двигательной активности (праксис), речь (умение построить собственную речь, а также понимание обращенной, способность к чтению, письму), возможность концентрации, сохранения работоспособности в течение определенного периода времени (внимание) и социальный интеллект (способность к пониманию и распознаванию эмоций, а также мотивов поведения других людей) [1, 2].
При определении тактики ведения пациентов основополагающим является не только выявление нарушенных КФ, но и оценка степени тяжести этих нарушений по сравнению с индивидуальной нормой [1–4]. Когнитивные нарушения (КН) подразделяют на когнитивные расстройства недементного типа (субъективные, легкие, умеренно выраженные КН) и деменцию [1–4]. Под субъективными КН понимают наличие жалоб у пациента на ухудшение КФ в отсутствие объективного подтверждения [1–6]. При легких когнитивных расстройствах жалобы пациента подтверждаются только при выполнении широкого специального нейропсихологического исследования [1–6]. Умеренные КН характеризуются возникновением затруднений в различных сложных видах интеллектуальной активности, однако при этом умеренные КН не оказывают выраженного влияния на профессиональную и бытовую сферы деятельности [1–6]. Деменция представляет собой тяжелое КН и характеризуется снижением одной или нескольких КФ, что не только сопровождается профессиональной и бытовой дезадаптацией пациента, но и приводит к снижению эффективности диагностических и терапевтических мероприятий в данной когорте [3, 5, 6].
Прогрессирование КН и развитие деменции являются значимой социально-экономической проблемой, в особенности удля лиц пожилого возраста: КН у таких пациентов сопровождается снижением продолжительности и качества жизни, в т.ч. из-за их социальной дезадаптации, а также увеличением инвалидизации [4, 7]. Пациенты испытывают трудности с выполнением рекомендаций врача из-за пропуска приема лекарственных препаратов или, наоборот, их передозировки, что приводит к росту числа госпитализаций и затрат на здравоохранение [4–8]. Достижения медицины способствовали возрастанию продолжительности жизни населения, что привело к увеличению доли пожилого населения. По оценкам исследователей, к 2050 г. число лиц пожилого возраста во всем мире будет составлять около 21% [9], а распространенность КН и деменции вследствие этого увеличится в 4 раза в ближайшие 50 лет, достигнув примерно 153 млн по сравнению с 57,4 млн пациентов на настоящий момент [7, 10].
В настоящее время отсутствуют эффективные методы лечения КН на стадии деменции, поэтому крайне важным представляется раннее выявление факторов риска развития КН на недементных стадиях, коррекция которых может потенциально предотвращать начало заболевания и/или замедлять темпы его прогрессирования [11–12].
Влияние артериальной гипертензии на состояние КФ, возникновение и прогрессирование КН и на риск деменции
Одним из основных и потенциально модифицируемых факторов риска развития КН и сосудистой деменции является артериальная гипертензия (АГ), поражающая головной мозг в качестве одного из органов-мишеней [11–13]. Частота встречаемости АГ увеличивается с возрастом, при этом ее распространенность возрастает с 27% у пациентов в возрасте моложе 60 лет до 74% у пациентов в возрасте старше 80 лет [14]. Фрамингемское исследование [15] показало, что более чем у 90% лиц с нормальным артериальным давлением (АД) в возрасте 55 лет в конечном итоге развивается АГ. Примерно у 60% населения к 60 годам диагностируется АГ, а к 70 годам этот показатель составляет 65% у мужчин и 75% у женщин [15]. В России распространенность АГ, согласно результатам исследования ЭССЕ-РФ (n=20 607, возраст участников на момент включения в программу 25–65 лет), при применении новых критериев составила 71,2% [16–17].
Частота развития КН у пациентов с АГ составляет 73,7% в отсутствие инсульта в анамнезе. В большинстве случаев КН являются легкими (46,7%) и умеренными (26,7%) [18]. Наиболее сильное негативное влияние АГ оказывает на такие КФ, как исполнительные функции, память и скорость обработки информации, а также абстрактное мышление [19].
В соответствии с клиническими рекомендациями Минздрава РФ/Российского кардиологического общества (РКО) уровень АД ассоциирован с риском возникновения КН и/или деменции [20]. Это подтверждается результатами ряда исследований, в которых выявлена взаимосвязь высокого уровня АД и/или факта наличия диагноза АГ со степенью снижения КФ у лиц пожилого и старческого возраста [21–24]. Так, согласно результатам Фрамингемского исследования [23] (n=1702, возраст – 55–88 лет), возрастание систолического (САД) и диастолического АД (ДАД) на каждые 10 мм рт.ст. у пациентов, не имевших в анамнезе инсульта и не принимавших антигипертензивную терапию (АГТ), ассоциировано со снижением КФ, в особенности внимания и памяти (с поправкой на возраст, образование, профессию, курение, употребление алкоголя, пол). Исследование HAAS (The Honolulu-Asia aging study) [24] также продемонстрировало связь между уровнем АД в среднем возрасте и развитием КН и деменции в пожилом возрасте. У пациентов, не принимавших АГТ, АГ была ассоциирована с высоким риском развития КН и/или деменции: отношение шансов – ОШ, 95% доверительный интервал – ДИ: 3,8 (1,6–8,7) для ДАД 90–94 мм рт.ст. и 4,3 (1,7–10,8) для уровня ДАД 95 мм рт.ст. и выше по сравнению с ДАД 80–89 мм рт.ст. [24]. А у пациентов с САД≥160 мм рт.ст. по сравнению с лицами с уровнем САД от 110 до 139 мм рт.ст. риск развития деменции был выше в 4,8 раза [24].
Согласно данным, полученным в проспективном когортном исследовании MAAS (The Maastricht Aging Study) [25] (n=1805, возраст пациентов на момент включения – 25–84 года), наличие у пациентов АГ, диагностированной на визите включения и возникшей в период наблюдения, статистически значимо ассоциировалось (р<0,01) с более быстрым снижением памяти и скорости обработки информации через 6 и 12 лет наблюдения. В исследовании ARIC (The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities) [22] (n=13 476, период наблюдения – 23 года) у пациентов с уровнем САД≥160 мм рт.ст. или ДАД ≥90 мм рт.ст. отмечено более выраженное снижение КФ, особенно скорости обработки информации, оперативной памяти и внимания. В исследовании I. Skoog et al. (n=382, период наблюдения – 15 лет) было показано, что пациенты в возрасте 79–85 лет с деменцией в возрасте 70 лет имели более высокие показатели САД (178 против 164 мм рт.ст.; p=0,034) и ДАД (101 против 92; p=0,004) по сравнению с теми, у кого деменция не развилась [26]. Это подтверждается и данными P.K. Elias et al. (n=529, период наблюдения – 20 лет), согласно которым более высокий уровень АД (повышение САД на каждые 10 мм рт.ст.) ассоциирован с более выраженными КН и снижением способности к пространственной визуализации [27].
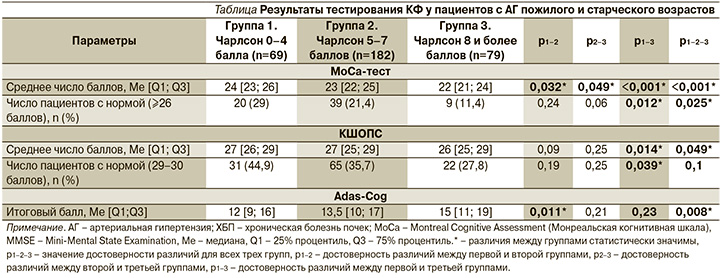
Существенный вклад в развитие КН у пациентов с АГ пожилого и старческого возраста вносят и сопутствующие заболевания. Полиморбидность является характерной чертой АГ у лиц старших возрастных групп. Так, под нашим наблюдением находилась когорта гериатрических пациентов с АГ (n=330), и мы оценили состояние их КФ в зависимости от числа баллов по шкале Чарлсон (шкала для оценки бремени полиморбидности). Для этого мы разделили пациентов на 3 группы: 1-я группа – 0–4 балла (69 пациентов), 2-я – 5–7 (182 пациента), 3-я группа – 8 и более баллов (79 пациентов). Согласно результатам когнитивных тестов, чем более выражена была полиморбидность (3-я группа), тем хуже были результаты МоСА-теста (сосудистые КН), краткой шкалы оценки психического статуса (КШОПС) и Adas-Cog (оба теста были созданы для скрининговой диагностики болезни Альцгеймера) (см.таблицу).
Возможности АГТ в профилактике развития и прогрессирования КН и деменции
Наиболее эффективным методом профилактики развития и прогрессирования КН и/или деменции у пациентов с АГ является применение АГТ [4, 10]. Основными классами лекарственных препаратов, использующихся в гипотензивных целях, согласно действующим клиническим рекомендациям, являются ингибиторы ангиотензинпревращающего фермента (иАПФ), блокаторы рецепторов ангиотензина (БРА), блокаторы кальциевых каналов (БКК), β-адреноблокаторы (БАБ) и диуретики, прежде всего тиазидные и тиазидоподобные, обладающие органопротективными свойствами [20]. В ряде эпидемиологических и обсервационных исследований было доказано, что АГТ снижает риск развития как инсульта, следовательно, и постинсультных когнитивных нарушений, так и КН, в т.ч. деменции [28–35].
По данным мета-анализа (136 исследований, 2 214 814 пациентов, средний возраст – 35,3–93,2 года, период наблюдения – 1,5–43 года) использование антигипертензивных препаратов (АГП) ассоциировалось со снижением риска развития деменции на 21% [28]. Это подтверждается результатами другого мета-анализа [29], согласно которому АГТ приводила к снижению риска деменции (скорректированное отношение шансов [ОШ]–сОШ=0,857, 95% доверительный интервал [ДИ]: 0,743–0,988) с поправкой на пол, возраст, уровень образование, наличие в анамнезе инсульта, индекс массы тела, наличие сопутствующего сахарного диабета.
Согласно результатам исследования EVA (Epidemiology of Vascular Aging, n=1373, средний возраст – 59–71 год, период наблюдения – 4 года), у пациентов, принимающих АГТ (ОШ=1,9; 95% ДИ: 0,8–4,4), снижение КФ было выражено в меньшей степени по сравнению с лицами без АГТ (ОШ=4,3; 95% ДИ: 2,1–8,8) [30].
Интересные данные получены в исследовании S. Köhler et al. [25]: даже у пациентов с контролируемой АГ на фоне АГТ (был достигнут и поддерживался целевой уровень АД) по сравнению с контрольной группой здоровых лиц с нормальным уровнем АД отмечено более быстрое снижение управляющих функций (р=0,017).
В группе пациентов с АГ, не принимавших АГТ, и в группе пациентов с неконтролируемой АГ на фоне АГТ (не достигших целевого уровня АД) по сравнению с группой больных контролируемой АГ выявлено более быстрое снижение памяти (р=0,003 и р<0,001 соответственно) и скорости обработки информации (р<0,001 для обеих групп сравнения), при этом неконтролируемая АГ также ассоциировалась со снижением управляющих функций (р<0,001) [25].
Согласно результатам рандомизированного двойного слепого плацебо-контролируемого исследования Syst-Eur (Systolic Hypertension in Europe) (n=2418, критерий включения, возраст ≥60 лет, медиана периода наблюдения – 2 года) в группе активной АГТ в конце периода наблюдения частота развития деменции была ниже на 50%: с 7,7 на 1000 пациенто-лет против 3,8 случая на 1000 пациенто-лет в группе плацебо (21 против 11 пациентов; p=0,05) [31]. Было рассчитано, что использование АГП у 1000 пациентов с АГ в течение 5 лет предотвращает 19 случаев деменции [31]. Более детально результаты этого исследования, а также исследования со сходным дизайном, проведенного в Китае, будут рассматриваться ниже в разделе статьи, посвященной влиянию отдельных классов АГП на КФ.
Способность АГТ снижать риск деменции была подтверждена и в многоцентровом рандомизированном клиническом исследовании SPRINT MIND (Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial-MIND) (n=9361, средний возраст – 67,9 года; медиана периода наблюдения – 5,11 года): достижение контроля АГ на фоне приема АГП (целевой уровень САД<120 мм рт.ст.) обеспечивало снижение риска развития как умеренных КН (отношение рисков [ОР]=0,81, 95% ДИ: 0,69–0,95), так и деменции (ОР=0,83, 95% ДИ: 0,67–1,04) по сравнению с уровнем САД 120–140 мм рт.ст. [33].
В исследовании PROGRESS (Perindopril Protection Against Recurrent Stroke Study) (n=6105, средний возраст – 64 года, период наблюдения – 3,9 года; периндоприл±индапамид против плацебо) была продемонстрирована способность АГТ уменьшать риск прогрессирования постинсультных КН и деменции на 45% (95% ДИ: 21–61) и 34% (95% ДИ: 3–55) соответственно [32]. Однако стоит упомянуть, что в исследовании PRoFESS (Prevention Regimen for Effectively Avoiding Second Strokes) (4937 пациентов, перенесших инсульт, средний возраст – 70–89 лет, период наблюдения – 3,7 года) в группе пациентов, принимавших АГТ (телмисартан), по сравнению с плацебо не было статистически значимых различий в частоте развития КН (p=0,98) [34].
В ряде других исследований, таких как SHEP (Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program) (n=4736, включали пациентов >60 лет, период наблюдения – 2,2 года) [35], HYVET-COG (Hypertension in Very Elderly Trial-Cognition) (n=1687, ≥80 лет, период наблюдения – 2,2 года) [36], TRANSCEND (Telmisartan Randomised Assessment Study in ACE intolerant subjects with cardiovascular Disease) (n=5926, ≥55 лет, период наблюдения – 4,7 года) [37], ONTARGET (The Ongoing Telmisartan Alone and in Combination with Ramipril Global Endpoint Trial) (n=25 620, ≥55 лет, период наблюдения – 4,7 года) [37], MRC (Medical Research Council trial of hypertension) (n=4396, возраст – 65–74 года, период наблюдения – 5,8 года) [38], не было выявлено статистическими значимого влияния АГТ на КФ, а частота развития КН и/или деменций не различалась между группами.
Противоречивые результаты вышеперечисленных исследований могут быть объяснены тем, что не только достижение целевых уровней АД на фоне лечения, но и сами АГП оказывают дополнительное церебропротективное действие, влияя на распространенность и выраженность изменений в сосудах головного мозга [10].
Так, по данным мета-анализа [39] (n=18 515 больных, средний возраст – 64±13 лет, период наблюдения – 1–54 месяца, медиана – 6 месяцев), прием АГП был статистически значимо ассоциирован с улучшением интегрального показателя, отражающего состояние КФ (размер эффекта – 0,05; 95% ДИ: 0,02–0,07) и всех отдельных КФ, кроме речи, а также сопровождался снижением риска развития деменции любого генеза на 9% по сравнению с контрольной группой (ОР=0,91; 95%ДИ: 0,89–0,94). Однако статистически значимой связи между гипотензивным эффектом препаратов и улучшением КФ не выявлено, что позволяет предположить наличие у АГП дополнительных церебропротективных механизмов. По данным авторов мета-анализа, при оценке влияния 5 основных классов АГП на КФ по сравнению с плацебо выявлен статистически значимый церебропротективный эффект только при приеме БРА (р=0,02) [39].
По данным А. Fournier et al. [40], наиболее выраженный эффект в плане профилактики развития и прогрессирования КН имеется у БКК и БРА, в то время как диуретики и иАПФ уменьшают развитие деменции только у пациентов с инсультом в анамнезе при условии их комбинированного применения. По результатам систематического обзора, БКК и иАПФ статистически значимо снижали вероятность развития когнитивного снижения или деменции в 2 из 6 анализируемых исследований, прием БРА – в 4 из 8 исследований, а диуретиков – в 3 из 8 изучаемых работ [41].
В последние годы показано, что АГТ может замедлять прогрессирование КН даже у лиц очень пожилого возраста (85 лет и старше) [42, 43]. Так, результаты популяционного когортного исследования Newcastle 85+ [42] (238 участников, возраст на момент включения – 85 лет, период наблюдения – 3 года) свидетельствуют о наличии статистически значимой взаимосвязи между применением БКК в качестве АГТ и снижением скорости прогрессирования КН по сравнению с другими классами АГТ (95% ДИ: 0,16–2,42; р=0,03, с поправкой на возраст, пол, уровень образования, курение, индекс массы тела, уровень АД и случаи инсульта/транзиторной ишемической атаки [ТИА] в анамнезе).
Аналогичные результаты получены в другом популяционном когортном исследовании Leiden 85-plus [43] (570 участников, возраст на момент включения – 85 лет, период наблюдения – 5 лет). Согласно полученным данным, только прием БКК ассоциировался со статистически значимым замедлением снижения КФ (p=0,001; после поправки на пол, возраст, прием других классов АГТ). При применении других АГП не было выявлено статистически значимого влияния на риск развития и прогрессирования КН и/или деменции (p>0,3) [43].
Как уже было упомянуто ранее, дигидропиридиновые БКК являются препаратами первой линии для лечения АГ [20]. Одним из наиболее эффективных представителей данного класса с доказанными органо-, в т.ч. церебропротективными, свойствами является нитрендипин. Помимо мощного антигипертензивного действия, за счет которого препарат можно принимать и для купирования резкого подъема АД, нитрендипин имеет дополнительные механизмы, препятствующие развитию КН и деменции [31, 44–50]. Так, D. Paris et al. [45] показали, что дигидропиридиновые БКК (нилвадипин – на момент подготовки материла не зарегистрирован в РФ, и нитрендипин, но не амлодипин) статистически значимо снижали уровни β-амилоида в головном мозге (экспериментальное исследование на мышиной модели), а также улучшали клиренс β-амилоида через гематоэнцефалический барьер. Помимо этого дисбаланс внутриклеточного кальция может играть важную роль в нейродегенерации, приводя к возникновению клеточной патологии и индуцируя апоптоз [47, 48]. Прием БКК, оказывая влияние на гомеостаз кальция, также потенциально может уменьшать развитие митохондриальной дисфункции и оксидативного стресса у пациентов с деменцией, в особенности имеющих мутацию в гене «пресенилин-1» (из-за которой накопление амилоида начинается в 20-летнем возрасте) [48]. Еще одним механизмом действия БКК, обеспечивающим профилактику развития и прогрессирования КН, является уменьшение концентрации кальция, что опосредованно приводит не только к снижению накопления β-амилоида, но и к уменьшению гиперфосфорилирования тау-протеина и гибели нейронов [49]. Другим механизмом церебропротективного действия нитрендипина является вазодилатация сосудов головного мозга путем блокировки нейрональных кальцевых каналов, а также опосредованное влияние на активность тромбоцитов, синтезирующих тромбин, являющийся основным источником β-амилоида [45, 50]. В исследовании BLSA (Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging) [51] (1092 пациента в возрасте >60 лет, период наблюдения – 19 лет) в группе пациентов, принимавших дигидропиридиновые БКК, была выявлена тенденция к снижению риска развития болезни Альцгеймера (ОР=0,30, 95% ДИ: 0,07–1,25; p=0,10).
Однако основным исследованием, в котором изучались органопротективные свойства нитрендипина в качестве АГП первой линии, является Syst-Eur, упомянутое ранее [31]. В исследовании приняли участие 4695 пациентов (возраст ≥60 лет, период наблюдения – 2 года), которые были рандомизированы в группу плацебо (n=2297) или приема нитрендипина в дозе 10–40 мг/сут (n=2398) с возможным добавлением иАПФ и диуретика, согласно двойному слепому методу. При оценке гипотензивного эффекта пациенты в группах нитрендипина и плацебо достигли целевых значений АД в 43,5 и 21,4% случаев соответственно (р<0,001), при этом когорта с контролируемой АГ в 60% принимала монотерапию нитрендипином [31]. В группе пациентов, принимавших нитрендипин, отмечалось значимое снижение риска развития фатального (на 42%; р=0,003) и нефатального инсульта (на 44%; р=0,007).
В исследовании также оценивался риск развития деменции и КН с использованием КШОПС. За 2-летний период наблюдения заболеваемость деменцией на фоне АГТ (нитрендипин±иАПФ, диуретик) снизилась на 50% по сравнению с плацебо [52].
Для оценки долгосрочных эффектов АГТ на основе нитрендипина была инициирована вторая фаза исследования SYST-EUR-II [53] (период наблюдения – 3,9 года). По результатам этого исследования у пациентов в группе нитрендипина (n=1485) по сравнению с плацебо (n=1417) риск развития деменции был статистически значимо ниже на 55% (3,3 и 7,4 случая на 1000 пациенто-лет соответственно; р<0,001), при этом отмечалось снижение частоты встречаемости не только болезни Альцгеймера (р<0,001), но и смешанной и сосудистой деменции (р<0,001) [53].
Аналогичное плацебо-контролируемое исследование The Syst-China trial (Systolic Hypertension in China) [54] было проведено в Китае (возраст >60 лет, медиана периода наблюдения – 3 года).
У пациентов в группе нитрендипина (±каптоприл, гидрохлоротиазид или оба препарата) (n=1253) по сравнению с плацебо (n=1141) риск развития инсультов был статистически значимо ниже на 38% (р<0,01), помимо этого частота смерти от всех причин, а также фатальных и нефатальных неблагоприятных сердечно-сосудистых событий была статистически значимо ниже в группе пациентов, получавших АГТ, основанную на нитрендипине, на 39% (р=0,003) и 37% (р=0,004) соответственно. По мнению авторов, прием АГТ в течение 5 лет может предотвращать развитие 39 инсультов, 59 серьезных сердечно-сосудистых осложнений или 55 смертей [54].
В рамках Всероссийской наблюдательной программы с международным участием КОГНИТА (КОГнитивные функции и НИТрендипин [Нитремед] при Артериальной гипертонии) [55] также оценивалось влияние нитрендипина на КФ и достижение целевых значений АД у пожилых пациентов с АГ. В исследование были включены 312 пациентов, которым в качестве моно- или комбинированной АГТ были назначены нитрендипин (Нитримед®, PRO.MED.CS Praha a.s., Czech Republic) (основная группа, n=252) или амлодипин (группа сравнения, n=60). Стартовая доза нитрендипина (Нитремеда) при назначении препарата в режиме монотерапии была 20 мг/сут с потенциальным увеличением до 40 мг/сут. Пациентам старческого возраста (≥80 лет) при назначении АК в составе комбинированной терапии стартовая доза нитрендипина равнялась 10 мг также с возможным увеличением до 20–40 мг/сут. Амлодипин при инициации терапии назначали в дозах, эквивалентных нитрендипину (5 мг/сут с возможным увеличением до 10 мг/сут) [55]. Когнитивный статус оценивали с помощью теста «Мини-Ког» (сумма менее 4 баллов расценивалась как высокая вероятность деменции) и МоСА (показатели менее 26 баллов трактовались как наличие КН), период наблюдения составил 1 год. За период наблюдения целевые показатели АД были достигнуты как в группе нитрендипина, так и в группе пациентов, принимавших амлодипин, в т.ч. в комбинации с индапамидом (Индап®, PRO.MED.CS Praha a.s., Czech Republic) [55].
На момент включения в исследование, согласно тесту Мини-Ког, наибольшее число лиц с КН как в когорте нитрендипина, так и в группе сравнения диагностировали в старших возрастных группах, что составило 10,9 и 13,8% у пациентов ≤65 лет, 23,8 и 27,8% – 65–74 года, 40 и 28,6% у лиц ≥75 лет, 47,8 и 33,3% – ≥80 лет соответственно. При оценке КФ через 12 месяцев наблюдения в группе нитрендипина отмечалось снижение числа пациентов с КН, согласно данному тесту: в возрастной подгруппе 65–74 года – с 23,8 до 4,55% (p=0,039), в возрастной группе ≥75 лет – с 40 до 8,6% (p<0,0001).
У пациентов, получавших амлодипин, уменьшение числа пациентов с КН выявлено только в подгруппе пациентов в возрасте 65–74 года с 27,8 до 0%, при этом оно оказалось статистически незначимым (p=0,063), а у пациентов ≥75 лет число таких пациентов осталось практически неизменным [55].
При анализе показателей теста МоСА установлено, что у пациентов пожилого и старческого возраста на момент включения исходные баллы были ниже 26, что трактовалось как КН (в когортах 65–74 года, ≥75 лет и ≥80 лет по шкале равнялся 24 [20; 26], 21,5 [19,5; 24,0] и 22 [20; 24] соответственно). При этом в группе пациентов, принимавших амлодипин, КН по результатам теста были выявлены только в группах ≥75 и ≥80 лет: 23 [19; 24] и 23 [19; 24] балла соответственно. Анализ КФ через 12 месяцев наблюдения показал статистически значимое увеличение медианы среднего балла за период исследования МоСА, который соответствовал, согласно критериям, норме (в возрастной группе 65–74 года с 24 [20; 26] до 27 [24; 29] баллов (p<0,0001), в группе ≥75 лет с 21,5 [19,5; 24,0] до 25,5 [23,5; 27,0] (p<0,0001) и в группе ≥80 лет с 22 [20; 24] до 26 [25; 27] баллов (p<0,0001) соответственно). Вместе с этим баллы во всех трех возрастных когортах пациентов, получавших амлодипин, через 12 месяцев наблюдения соответствовали наличию КН [55].
Диуретики (в подавляющем большинстве случаев тиазидные и тиазидоподобные) – еще один основной класс АГП, они занимают важное место в рациональной фармакотерапии АГ [20]. Уникальным представителем данного класса является индапамид, относящийся к тиазидоподобных диуретикам. Этот препарат не только имеет превосходящую другие препараты длительность действия, равную 24 часам, но и обладает двойным механизмом гипотензивного эффекта: помимо стимуляции диуреза и натрийуреза индапамид является периферическим вазодилататором [20, 56–58], чем и обусловлен его органопротективный эффект, доказанный в ряде клинических исследований, часть из которых обсуждена выше.
По данным мета-анализа [56] (52 599 человек, средний возраст – 76,1 года, медиана периода наблюдения – 6,1 года), применение диуретиков было ассоциировано со снижением риска развития деменции (ОР=0,83, 95% ДИ: 0,76–0,91; р<0,0001) и деменции при болезни Альцгеймера (ОР=0,82, 95% ДИ: 0,71–0,94; р=0,004). Представляет интерес тот факт, что в качестве одного из церебротективных механизмов диуретиков авторы рассматривают повышение уровня мочевой кислоты в сыворотке крови, что может приводить к уменьшению риска развития КН и деменции [56].
Важнейшим механизмом действия индапамида, обеспечивающим профилактику КН, является снижение продукции β-амилоида, а также опосредованное улучшение морфофункциональных свойств мозговых артериол за счет уменьшения процессов гипертрофического ремоделирования сосудистой стенки [57, 58].
По данным другого мета-анализа [59] (n=112113, средний возраст – 66,4 года), в группе больных, принимавших диуретики, по сравнению с группой контроля была статически значимо ниже частота возникновения сердечно-сосудистых событий (ОШ=0,86; р=0,007) и сердечной недостаточности (ОШ=0,62; р<0,001), однако прием АГТ не оказывал влияния на риск развития инсульта (ОШ=0,92; р=0,438) и ишемической болезни сердца (ОШ=0,95; р=0,378). При раздельной оценке классов диуретиков было продемонстрировано, что на фоне приема тиазидоподобных диуретиков, в т.ч. индапамида, отмечалось снижение риска не только неблагоприятных сердечно-сосудистых событий (ОШ=0,78; р<0,001) и сердечной недостаточности (ОШ=0,57; р<0,001), но и инсульта (ОШ=0,82; р=0,0016) по сравнению не только с плацебо, но и с группой больных, получавших в качестве АГТ тиазидные диуретики [59].
Двойное слепое плацебо-контролируемое исследование PROGRESS [60] (n=6105) показало, что среди пациентов, перенесших инсульт или ТИА, АГТ снижает риск повторного инсульта на 28%. Пациенты были распределены в группы монотерапии периндоприлом, комбинированной терапии периндоприла и индапамида и плацебо. Согласно полученным результатам, комбинированная АГТ снижала как уровень АД на 12/5 мм рт.ст., так и риск инсульта на 43% (p<0,01), в то время как прием только периндоприла приводил к снижению АД на 5/3 мм рт.ст. и не оказывал влияния на риск повторного инсульта (ОР=95%; 95% ДИ: 19–23%). Кроме того, в группе комбинированной АГТ риск развития постинсультной деменции был ниже примерно на 50% по сравнению с группой монотерапии иАПФ [60].
В рандомизированном двойном слепом плацебо-контролируемом исследовании PATS (Post-stroke Antihypertensive Treatment Study) [61] (n=5665; с инсультом или ТИА в анамнезе, период наблюдения – 2 года), в котором оценивалось влияние АГТ на риск развития фатального и нефатального инсультов, все пациенты были рандомизированы в группы, получавшие монотерапию индапамидом 2,5 мг или плацебо. Согласно полученным данным, риск развития инсульта в когорте пациентов с АГТ был статистически значимо ниже по сравнению с группой плацебо (ОР=0,71; р=0,0009), при этом частота развития инсульта в группе индапамида составляла 9,4 случая на 100 пациентов, в группе плацебо – 12,3 на 100. Авторы рассчитали, что прием индапамида в течение 3 лет позволяет предотвращать 29 инсультов на 1000 пациентов [61].
Приведенные выше данные позволяют рассматривать нитрендипин, а также индапамид в качестве препаратов первого выбора для профилактики снижения КН и развития деменции у пожилых пациентов с АГ и для церебропротекции в целом.
Заключение
В настоящий момент опубликованы результаты достаточно большого числа исследований, подтверждающих влияние АГП на снижение риска развития и прогрессирования КН и/или деменции. Наиболее доказанными классами АГТ, обладающими церебропротективным эффектом, являются блокаторы кальциевых каналов и диуретики, в частности их представители нитрендипин и индапамид. Являясь препаратами первого выбора у пациентов с АГ пожилого и старческого возраста, в т.ч. с инсультом в анамнезе, данные препараты широко представлены на фармацевтическом рынке РФ и доступны в виде лекарственных средств Индап® и Нитремед®. С учетом их значимых органопротективных эффектов, в т.ч. церебропротективного, а также нахождения в оптимальном ценовом диапазоне следует повышать информированность практикующих врачей о проведении рациональной фармакотерапии пациентов пожилого и старческого возраста.
Дополнительная информация
Публикация статьи осуществляется в рамках диссертационных работ:
- Дзамихов К.К. «Когнитивный статус полиморбидных пациентов с артериальной гипертензией и фибрилляцией предсердий»;
- Телкова С.С. «Клиническая значимость анемии, дефицита железа и витамина В12 у пациентов с фибрилляцией предсердий, перенесших острый коронарный синдром».


