Введение
Несмотря на развитие и эффективность интервенционной аритмологии отказ от применения лекарственных антиаритмических средств не может быть реализован в полном объеме [1]. В cовременной клинической практике целесообразным представляется назначение только тех антиаритмических препаратов, которые подтвердили свою безопасность и эффективность в хорошо организованных рандомизированных доказательных исследованиях. Вместе с тем не всегда представляется возможным в конкретной клинической ситуации оценить безопасность планируемой антиаритмической терапии для данного пациента [1].
Одним из антиаритмиков, вызывающих у эндокринологов наиболее противоречивые чувства, является препарат III класса по классификации антиаритмических средств Вогана–Вильямса амиодарон.
Амиодарон – производное бензофурана, по своему химическому строению сходный с молекулой тироксина [2, 3].
Патологическое воздействие препарата на тиреоциты имеет несколько причин. Одна из них заключается в том, что в 200 мг препарата содержится 75 мг (75 тыс. мкг) йода. Это составляет 50000% от суточной потребности в йоде взрослого человека. Даже при условии, что из 200 мг амиодарона усваивается только 6 мг (600 мкг), это составляет «всего» 400% от суточной потребности в йоде [4]. При пероральном приеме процесс выведения амиодарона носит двухфазный характер. В момент первой фазы препарат выводится за 4–21 час. Время выведения во 2-й фазе растягивается до 25–110 дней. Амиодарон метаболизируется в печени, превращаясь в активный метаболит дезэтиламиодарон, который вместе с амиодароном накапливается в тканях [4]. Когда прием амиодарона прекращен, последующее выведение препарата из организма может достигать нескольких месяцев [4]. К отягчающим факторам, еще более затрудняющим выведение препарата из организма, относятся ожирение (уменьшение выведения на 22%) и пожилой возраст (соответственно на 46%) [5].
Согласно клиническим рекомендациям Российского кардиологического общества, применение амиодарона при различных формах нарушения ритма обоснованно и в некоторых клинических ситуациях высокоэффективно. Вместе с тем, согласно инструкции к препарату, амиодарон абсолютно противопоказан при гипо- и гипертиреозе [4], наличие которых у пациента невозможно достоверно выявить в экстренном случае за ограниченное время. Перед началом терапии амиодароном необходимо определить исходный уровень тиреотропного гормона (ТТГ), антитиреоидные антитела и провести ультразвуковое исследование (УЗИ).
К сожалению, применение амиодарона обычно является решением в неотложной клинической ситуации, когда нет возможности выполнить исследование состояния щитовидной железы (ЩЖ). Таким пациентам следует его провести сразу после введения амиодарона при первой возможности [6].
В результате, несмотря на побочные эффекты, амиодарон все-таки остается одним из наиболее эффективных антиаритмических средств и широко применяется в клинической практике [6–9].
Влияние амиодарона на функционирование ЩЖ
Большинство пациентов, начавших терапию амиодароном, остаются в эутиреоидном состоянии, даже если используются высокие дозы препарата (400 мг в сутки) [10], частота возникновения амиодарон-индуцированного тиреотоксикоза (АмИТ), по разным статистическим данным, варьируется от 1 до 23% [11–13].
Тиреотоксикоз, вызванный применением амиодарона, разделяют на 3 типа: 1-й тип обусловлен повышенной продукцией гормонов ЩЖ, при 2-м типе тиреотоксикоз носит деструктивный характер (т.е. возникает вследствие разрушения ткани ЩЖ с выходом ее гормонов в кровь). Также выделяют наиболее сложный промежуточный тип: смешанный [2, 14].
При назначении амиодарона многие врачи хотят быть уверенными в преобладании пользы над риском.
В различных рекомендациях обсуждаются предикторы развития дисфункции ЩЖ после старта терапии амиодароном. Так, определение соотношения концентрации активного метаболита амиодарона к его содержанию в крови (ДЭАм/Ам) может быть тем параметром, который позволит прогнозировать развитие АмИТ: при развитии данного состояния это соотношение повышается [2, 15].
Эти данные подтверждаются японским ретроспективным исследованием, в котором приняли участие 377 человек. Пациентам, получавшим амиодарон с января 2012 по апрель 2016 г., проводилось исследование тиреоидного статуса, определение концентрации амиодарона, дезэтиламиодарона и ДЭАм/Ам. Среди участников этого исследования частота АмИТ и гипотиреоза составила 14,3 и 15,9% соответственно. В результате повышение соотношения ДЭАм/Ам даже до начала возникновения АмИТ было обнаружено у 54 больных с выявленным в последующем тиреотоксикозом.
И при определении тиреотоксикоза эта концентрация значительно возросла (рис. 1) [15].
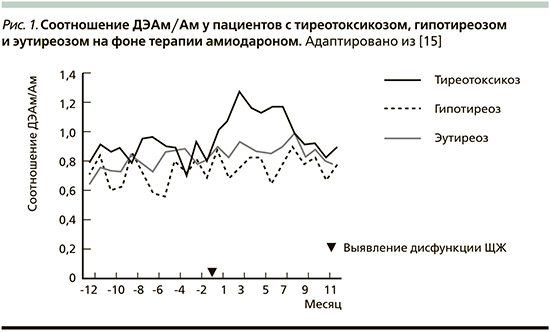
По данным других исследователей специфических предикторов возникновения дисфункции ЩЖ, связанной с приемом амиодарона, выявить не удалось [16, 17].
Среди диагностических инструментов для прогнозирования возникновения АмИТ 2-го типа были попытки применения компьютерной томографии (КТ). Группа ученых из Бельгии изучила нативную плотность у пациентов, принимавших амиодарон, после того как при проведении КТ у пациента с АмИТ 2-го типа была выявлена «белая» ЩЖ. У пациентов с эутиреозом плотность была высокой (34 пациента) и очень высокой у 20 больных АмИТ 2-го типа по сравнению с группой контроля (24 человека). Это может быть связано с накоплением йода в лизосомах тиреоцитов, но, к сожалению, не позволяет уверенно разделить АмИТ 1-го и 2-го типов [17].
Патогенез АмИТ
Физиологическая адаптация ЩЖ к избыточному поступлению йода из внешней среды обусловлена тем, что в условиях гиперйодидемии возникает временная блокировка органификации йода и снижение образования тиреоидных гормонов в течение нескольких недель с одновременным ростом ТТГ [18]. Этот адаптационный процесс носит название «эффект Вольфа–Чайкова». Далее, несмотря на продолжающееся избыточное поступление йода, блокировка синтеза тиреоидных гормонов прекращается и наступает т.н. эффект ускользания – не зависимый от уровня ТТГ процесс, провоцируемый интратиреоидным снижением содержания йода [18].
В результате воздействия амиодарона возникает йод-индуцированная активация оксидативного стресса, блокируется дейодиназа 1-го типа в периферических тканях и дейодиназа 2-го типа в гипоталамо-гипофизарной области, а также в 2 раза снижается конверсия Т4 в Т3, что вызывает возрастание уровня Т4 и неактивного реверсивного Т3. Наряду с этим при применении амиодарона происходит нарушение связывания Т3 с рецепторным аппаратом. Подобные изменения по принципу обратной связи приводят к компенсаторному повышению концентрации ТТГ [19, 20].
Все вышеизложенное наводит на следующую мысль: функция ЩЖ на фоне применения амиодарона может снижаться с развитием манифестного гипотиреоза. Возникновение же тиреотоксикоза на терапии амиодароном – процесс до конца не ясный, нуждающийся в осмыслении причин и механизмов развития. Известно, что развивается он в йододефицитных районах, в 3 раза чаще у мужчин и протекает по трем различным сценариям (рис. 2).
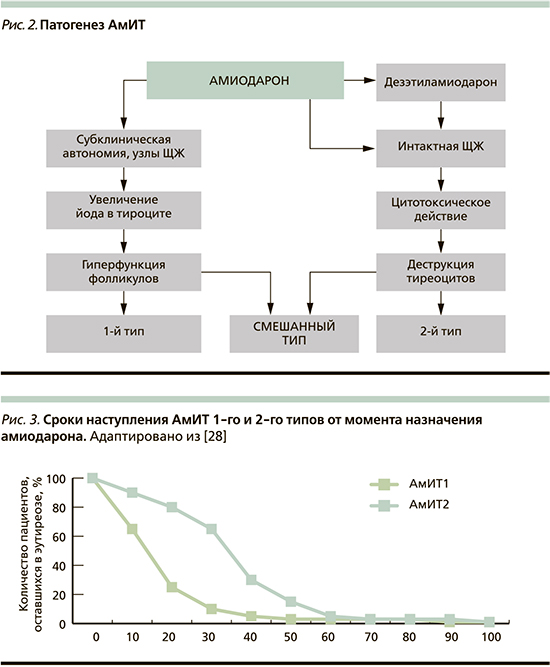
АмИТ 2-го типа, или деструктивный тиреоидит, возникает в интактной ЩЖ вследствие прямого цитотоксического действия амиодарона на тиреоциты – сам препарат и его активный метаболит дезэтиламиодарон обладают дозозависимым свойством повреждать фолликулы ЩЖ [20, 21]. Это находит свое подтверждение в патоморфологическом исследовании структуры ЩЖ: выявляются нарушение нормальной архитектоники тиреоидной ткани, некроз и апоптоз, отложение в тиреоцитах липофусцина, наличие включений и расширение эндоплазматической сети [17].
АмИТ 1-го типа, как правило, возникает у пациентов с изначально измененной ЩЖ: фоновой автономией ЩЖ при узловом или недиагностированном диффузном токсическом зобе (в самом начальном, доклиническим, его состоянии), особенно в условиях дефицита йода [9, 21, 22]. Принято считать, что при данном типе тирео-токсикоза йод, высвобождаемый из препарата, индуцирует гиперактивность фолликулов и синтез гормонов ЩЖ в зонах автономии или стимулирует имеющийся аутоиммунный процесс [14]. (Упоминающийся по этому поводу в литературе термин «Йод-Базедов», не совсем верен, поскольку то патологическое состояние, которое описали фон Базедов и Грейвс, было по сути классическим диффузным токсическим зобом, не индуцированным приемом йода [23]).
Таким образом, возникновение АмИТ 1-го типа является многофакторным процессом, в котором играют роль не только избыточное поступление йода при ранее имеющимся йододефиците, но и генетические аспекты и преморбидный фон пациента.
Смешанный тип АмИТ развивается, когда у пациентов одновременно развиваются два патогенетических механизма, характерных для АмИТ 1-го и 2-го типов, т.е. сочетание деструкции фолликулярного аппарата ЩЖ вместе с гиперпродукцией тиреоидных гормонов, что делает диагностику этого состояния весьма затруднительной [2, 11, 21, 22, 24, 25].
Аспекты диагностики АмИТ
Диагностика АмИТ в соответствии с различными рекомендациями заключается в учете факта приема данного лекарственного препарата при наличии клинико-лабораторных признаков тиреотоксикоза [2, 22].
Вместе с тем дифференциальный диагноз различных типов АмИТ зачастую представляет собой трудоемкий и не всегда результативный алгоритм.
Подтверждением изначальной ошибки в типировании АмИТ является неэффективность предпринятой антитиреоидной стратегии лечения [26, 27]. Так, при наблюдении за пациентами с АмИТ установлено, что эффективность т.н. типоспецифичной терапии (тиреостатики при 1-м типе и глюкокортикостероиды [ГКС] при 2-м) была результативной для 58% пациентов с деструктивным механизмом его развития и 36% больных с продуктивным механизмом тиреотоксикоза [27].
Недавний ретроспективный анализ исследования с включенными 200 пациентами с АмИТ показал, что тиреотоксикоз развивался значительно раньше при 1-м типе [медиана – 3,5 месяца, диапазон – 1,0–61,0], чем при 2-м [медиана – 30,0 месяцев, диапазон – 1,0–95,0; p< 0,001] (рис. 3) [28].
Поскольку в этом исследовании у 80% больных АмИТ 1-го типа были автономные узлы ЩЖ, неудивительно, что йод-индуцированный тиреотоксикоз развился в начале курса терапии амиодароном. На основании полученных данных можно предположить, что у пациента с поздним началом АмИТ, у которого исключен диффузный токсический зоб, с высокой вероятностью имеет место деструктивный тип тирео-токсикоза – АмИТ 2-го типа. Еще одним результатом этого исследования стало наблюдение, согдасно которому АмИТ 2-го типа может развиваться после прекращения приема амиодарона: у 19% пациентов АмИТ 2-го типа манифестировал в среднем через 5,5 месяцев после окончания приема препарата [9, 26].
Сцинтиграфия
Для оценки функционального состояния ЩЖ в настоящее время доступны три различных радиофармпрепарата (РФП), в т.ч. радиоактивный йод (РАИ) с 131I или 123I, технеция 99m пертехнетат (99mTcO4-) и 99mTc-метокси-изобутил-изонитрил (99mTc-технетрил) [2]. Принято считать, что продуктивные виды тиреотоксикоза (в т.ч. и АмИТ 1-го типа) сопровождаются повышением накопления РФП, а деструктивные (включая АмИТ 2-го типа) – резко сниженным [21]. Вместе с тем в областях с исходно низким/погранично низким потреблением йода сцинтиграфическая картина при АмИТ 1-го типа может быть с низким, нормальным или даже высоким суточным поглощением РАИ, тогда как при АмИТ 2-го типа этот показатель в основном равен нулю. В настоящее время для типирования данного вида тиреотоксикоза наиболее информативна сцинтиграфия с 99mTc-технетрилом. В результате проведенного исследования Piga среди 20 пациентов с АмИТ установлено, что у больных АмИТ 1-го типа захват был нормальным или повышенным (A), при АмИТ 2-го типа отсутствовал (C), тогда как при смешанном варианте поглощение РФП было весьма небольшым, но стойким или происходило быстрое вымывание (B) (рис. 4) [2, 30].
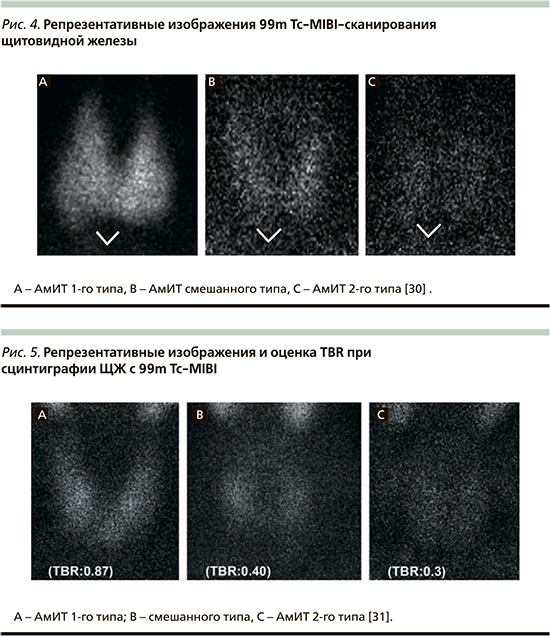
Полученные результаты нашли подтверждение в более позднем и дополненном исследовании Censi – в этом случае 30 пациентам с АмИТ различных типов проводили не только сцинтиграфию ЩЖ с технетрилом, но и полуколичественный анализ поглощенного РФП – target-to-background ratio (TBR). В результате установлено, что у пациентов с АмИТ 1-го типа наблюдалась отчетливая диффузная задержка РФП, у пациентов с АмИТ 2-го типа значительного поглощения не наблюдалось, в то время как у остальных шести обнаружено несколько более высокое поглощение, чем при АмИТ 2-го типа, таким образом сцинтиграфически они были классифицированы как случаи смешанного АмИТ [31]. При оценке полуколичественного поглощения РФП анализ ROC-кривой выявил пороговое значение TBR 0,482 для различения АмИТ 1-го и 2-го типов со 100%-ной специфичностью и 91,7%-ной чувствительностью (р<0,0001, AUC: 0,982). Фактически у 11 из 12 пациентов с АмИТ 2-го типа TBR был ≤0,482, у всех 14 пациентов с первым типом АмИТ TBR был >0,482. С другой стороны, TBR не смог идентифицировать четыре смешанные формы АмИТ (рис. 5) [31].
По современным данным, сцинтиграфия ЩЖ с [99mTc]2-метоксиизобутилизонитрилом (MIBI) предложена в качестве полезного диагностического инструмента при исследовании пациентов с различными типами АмИТ [22, 30].
УЗИ
Цветное допплеровское картирование (ЦДК) обеспечивает неинвазивную оценку васкуляризации ЩЖ в режиме реального времени [24]. Согласно клиническим рекомендациям Российской Ассоциации эндокринологов (РАЭ), этот метод является основным для дифференциальной диагностики типов АмИТ [2].
Целесообразно применение следующего протокола диагностики различных типов АмИТ по ЦДК.
«Образец 0» – отсутствие васкуляризации или единичные точечные участки кровотока при исследовании ЩЖ (рис. 6) [32].
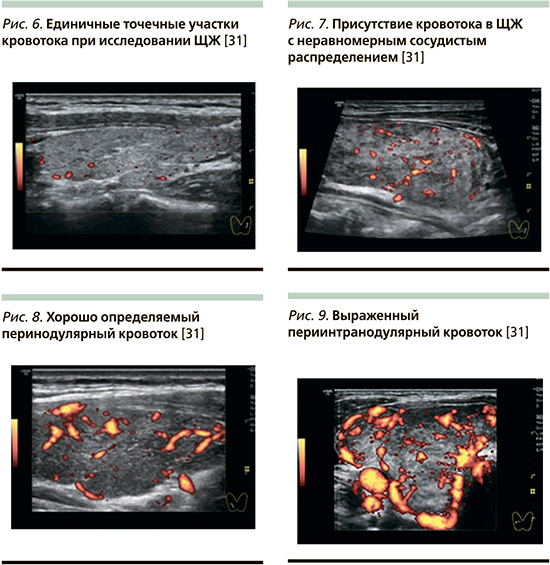
«Образец I» – присутствие кровотока в ЩЖ c неравномерным сосудистым распределением или васкуляризацией внутри узла (рис. 7) [32].
«Образец II» – небольшое усиление кровотока с неравномерной васкуляризацией или хорошо определяемый перинодулярный кровоток (рис. 8) [32].
«Образец III» – значительное усиление васкуляризации с однородным кровотоком или выраженный периинтранодулярный кровоток (рис. 9) [32].
При исследовании пациентов с АмИТ при 1-м типе определялись образцы I–III, при 2-м – 0 [2]. Вместе с тем диагностика смешанного варианта АмИТ с помощью ЦДК невозможна. По результатам шести различных исследований чувствительность и специфичность ЦДК для дифференциальной диагностики 1-го и 2-го типов АмИТ составили соответственно 96,8–93,6% и 94,1–90,1% [24, 27, 30].
Однако достоверность этих данных подтверждается не всеми исследователями [25, 27, 33, 34].
Действительно, проведено изучение 24 пациентов, где после определения сниженной васкуляризации при ЦДК у 12 установили АмИТ 2-го типа. Однако после инициации терапии ГКС у этих пациентов только 7% получили эффект от проводимого лечения [27].
Похожее исследование, но уже с повышенной васкуляризацией при ЦДК выявило, что среди 11 пациентов только 36% ответили на терапию тиреостатиками. В другой серии исследований из 30 больных АмИТ 33% не могли быть отнесены к тому или иному типу на основании ЦДК (пациенты, к примеру, могли иметь зоб ЩЖ, но нормальную васкуляризацию при ЦДК) [25].
Таким образом, ни один из методов визуализации, применяемый сам по себе, не может точно типировать АмИТ, а значит, стать основой выбора наилучшей стратегии лечения, что частично объясняется наличием смешанной формы заболевания [22].
Возникает вопрос: какие лабораторные методы исследования могут помочь в этой непростой ситуации? Многочисленные попытки определить некие биохимические маркеры пока не увенчались успехом. Так, изучение тиреоглобулина показало, что он может быть повышен при АмИТ как 1-го типа (вследствие аутоиммунного процесса), так и 2-го (в результате деструкции фолликулов ЩЖ) [29].
По другим данным, может быть полезным изучение расчетного соотношения свободного (св.) Т4 к св.Т3 [14]. Исследование, проведенное коллегами из НМИЦ им. В.А. Алмазова, показало, что у 75% больных АмИТ 1-го типа соотношение св.Т4/св.Т3 <3,10, в то время как у 75% больных АмИТ 2-го типа соотношение св.Т4/св.Т3 > 3,65 [35]. Однако другие исследователи, изучавшие обратное отношение Т3 к Т4, которое, как правило, выше у пациентов с АмИТ 1-го типа, чем у пациентов с деструктивным тиреоидитом, считают, что этот показатель не имеет клинического значения ввиду связанного с амиодароном ингибирования монодейодирования Т4 [2].
Наличие антител к рецептору ТТГ свидетельствует о диффузном токсическом зобе, следовательно, об АмИТ 1-го типа [2, 19]. Вместе с тем в современной клинической и лабораторной практике не происходит разделения на тиреоблокирующие и тиреостимулирующие антитела, и, по данным некоторых исследователей, у больных гипотиреозом с хроническим атрофическим тиреоидитом антитела блокирующего типа выявляют в 16–40% случаев. Более того, данный вид антител иногда бывает положительным у пациентов с деструктивным тиреоидитом [36]. Наряду с этим по результатам проспективного исследования Safran не было обнаружено повышения уровня антитиреоидных антител у пациентов, получавших амиодарон в США и Италии [37]. Таким образом, уровень антител к рецептору ТТГ следует осторожно интерпретировать при дифференциальной диагностике между АмИТ 1-го и 2-го типов, поскольку он может быть положительным у пациентов с латентной болезнью Грейвса (1-й тип), а также при деструктивном тиреоидите, ассоциированном с амиодароном (2-й тип).
В качестве маркера АмИТ 2-го типа активно обсуждается и интерлейкин-6 (ИЛ-6), который значительно увеличивается при этой тиреопатии [26, 29, 38]. Однако повышение этого параметра характерно и для хронической сердечной недостаточности, диффузного токсического зоба, и для ожирения, что заметно снижает ценность данного показателя [29, 38].
По последним данным, на сегодняшний день ни один из изученных сывороточных маркеров – ни высокочувствительный С-реактивный белок, ни ИЛ-6 – не являются достоверными информативными маркерами для дифференциальной диагностики АмИТ 1-го и 2-го типов [9, 17].
С целью улучшить верификацию разных типов АмИТ проведено исследование, связанное с определением уровня β-глюкуронидазы (β-G) – лизосомального фермента, высвобождаемого в кровоток в случае воспаления, у пациентов с тиреоидитами. У 9 пациентов с АмИТ 1-го типа и 9 с АмИТ 2-го исследовали данный показатель по сравнению контрольной группой (21 человек), а также 14 пациентами с тиреотоксикозом другой этиологии и больными подострым тиреоидитом (14 больных) [27]. На основании этого исследования авторы сделали вывод, согласно которому повышение уровня β-G отмечалось именно у больных деструктивным тиреотоксикозом (АмИТ 2-го типа и тиреоидит де Кервена) [27].
С учетом сочетания двух совершенно разнонаправленных патологический процессов смешанный вариант АмИТ, происходящих в ЩЖ, видимо, более вероятен, когда результаты лабораторно-инструментальных исследований противоречат друг другу [2, 4]. Возможно также опираться на результаты сцинтиграфии с 99m Tc-MIBI [30, 31]. В ряде случаев динамическое наблюдение пациентов позволяет реклассифицировать тип АмИТ по ответу на проводимую терапию ГКС или после наступления перманентного гипотиреоза, маловероятен при продуктивном тиреотоксикозе.
Терапия АмИТ
Лечение АмИТ должно носить патогенетический характер и определяться типом развившейся тиреоидной дисфункции у пациента.
В случае АмИТ 1-го типа рекомендована терапия тиреостатиками, обоснованная гиперпродукцией тиреоидных гормонов. Причем дозы тиреостатиков ввиду резистентности данного вида тиреотоксикоза должны быть выше привычных, применяемых при диффузном токсическом зобе (тиамазол 40–60 мг в 2 приема, пропилтиоурацил – 400–600 мг в сутки).
Такие высокие суточные дозы обусловлены устойчивостью к терапии ввиду высокого накопления интратиреоидного йода при АмИТ 1-го типа [2, 22]. Доза может быть уменьшена только через 6–12 недель, но продолжительность тирестатической терапии в целом нередко бывает весьма длительной.
С учетом резистентности к тиреостатической терапии в ряде случаев возникает необходимость применения дополнительных лекарственных препаратов для достижения эутиреоза. Для повышения чувствительности ЩЖ к тионамидам американское эндокринологическое сообщество рекомендует использовать перхлорат калия или натрия, который блокирует активное поступление йода в ЩЖ за счет ингибирования натрий/йодного ко-транспортера. В результате интратиреоидное содержание йода уменьшается, а терапевтический эффект тионамидов усиливается [11].
В Российской Федерации перхлораты калия и натрия не зарегистрированы, альтернативным решением предлагается дополнительное назначение препаратов лития [2].
Из-за способности карбоната лития накапливаться в ЩЖ снижаются синтез и секреция тиреоидных гормонов вследствие изменения самой структуры тиреоглобулина и нарушения процессов образования йодтиронинов [39]. Карбонат лития назначают в дозе 300 мг каждые 6–8 часов, и получить эффект удается уже к концу 1-й–началу 2-й недели. Однако в аннотации к препарату не указана дисфункция ЩЖ, таким образом, назначение карбоната лития в данном случае проводится «off label» и требует правильного оформления в виде проведения консилиума и подписания дополнительного информированного согласия пациентом [2, 4]. После достижения эутиреоза у пациентов с АмИТ 2-го типа должен последовать следующий этап лечения – абляция ЩЖ (оперативное лечение или радиойодтерапия [РЙТ]). Радиойодтерапия для лечения АмИТ 1-го типа может быть назначена через 6–12 месяцев после отмены амиодарона [2]. Косвенным подтверждением возможности выполнения РЙТ будет нормализация экскреции йода с мочой и накопление РФП на сцинтиграфии.
Больным АмИТ 2-го типа рекомендована терапия ГКС, несмотря на т.н. транзиторность деструктивных видов тиреотоксикоза, ввиду пагубного воздействия избытка тиреоидных гормонов на сердечно-сосудистую систему пациента. Препаратом выбора в данном случае является преднизолон в суточной дозе 30–40 мг, длительность терапии – 2–3 месяца. После достижения эутиреоза дозу преднизолона начинают постепенно уменьшать по общим правилам снижения и отмены ГКС [2, 4, 26]. В результате перорального приема ГКС примерно у 20% больных достижение эутиреоза в среднем происходит лишь через 90 дней. Такой длительный период времени часто не приемлем для пациентов с сопутствующими тяжелыми сердечными заболеваниями. К сожалению, из-за деструктивного процесса, лежащего в основе АмИТ 2-го типа, терапия РАИ практически неэффективна, вместе с тем срочная тотальная тиреоидэктомия на фоне тяжелого тиреотоксикоза часто слишком рискованна [40]. Недавно было предложено внутривенное введение ГКС для лечения пациентов с АмИТ 2-го типа и тяжелым тиреотоксикозом в режиме пульс-терапии метилпреднизолоном в дозах 400–800 мг [40]. Подобный подход рассматривается как альтернатива срочной тотальной тиреоидэктомии, которая быстро восстанавливает эутиреоз у отдельных пациентов с резистентным АмИТ и быстро ухудшающейся сердечной функцией. Однако пока пульс-терапия ГКС по сравнению с их пероральным приемом имеет противоречивые результаты и нуждается в дальнейших исследованиях [2, 4, 41].
В случае подозрения на смешанный вариант АмИТ рекомендована сочетанная терапия тиреостатическими препаратами и ГКС [2, 4].
При этом существуют различные подходы к старту терапии: в европейских рекомендациях при подозрении на смешанный тип АмИТ инициацию терапии последовательно начинают с тиреостатиков и при их малой эффективности через 4–6 недель рассмотривают вопрос о присоединении ГКС [22]. По рекомендациям Американской тиреоидологической ассоциации следует рассмотреть возможность начальной комбинированной терапии пациентов с умеренным тиреотоксикозом и сопутствующей кардиальной патологией [9].
Некоторые медицинские сообщества рекомендуют начинать комбинированную терапию тиреостатиками и ГКС как еще один способ типировать АмИТ [16]. Так, если после 2 недель комбинированной терапии уровень св. Т3 у больного снизится более чем на 50% от исходного, вероятно, речь идет о АмИТ 2-го типа, в связи с чем следует отменить тионамиды и продолжить терапию преднизолоном. В случае повышения концентрации св. Т3 более вероятным представляется АмИТ 1-го типа, что ведет за собой отмену преднизолона и продолжение терапии тионамидами [3]. В клиническом руководстве британских эндокринологов рекомендуется не отменять амиодарон в случае развития АмИТ и начинать сочетанную терапию ГКС и карбимазолом, в случае, если через 2 недели уровни T3 не снизились, добавить перхлорат калия [42]. Согласно алгоритмам турецких эндокринологов, амиодарон в случае АмИТ все-таки отменяется, а терапия начинается с перхлората калия в сочетании с метимазолом, и если через 30 дней св. T4 не нормализовался или не снизился более чем на 50%, необходимо добавить ГКС [43].
В ряде случаев АмИТ «типоспецифичная» даже смешанная терапия не эффективна на фоне ухудшающегося состояния пациента из-за прогрессирования кардиальной патологии. Уже рассмотрен вариант пульс-терапии ГКС, но его применение даже при АмИТ 2-го типа дает противоречивые результаты, что заставляет прибегать к более радикальным методам лечения [44, 45]. Один из таких методов – неотложная тиреоидэктомия [2, 4]. Разумеется, выполнение оперативного вмешательства на фоне тяжелой кардиальной патологии у пациентов в состоянии тиреотоксикоза влечет за собой довольно высокие риски осложнений, включая летальный исход. Однако в каждой конкретной ситуации требуется взвешивать риски от оперативного вмешательства и риски дальнейшего сохранения тиреоидной дисфункции у пациента в течение неопределенно длительного времени. Так, по данным D. Cappellani, летальность была меньше у пациентов с тяжелой систолической дисфункцией и проведенным оперативным вмешательством, чем у таковых со сходной кардиальной патологией на фоне медикаментозной терапии [46].
Заключение
Дисфункция ЩЖ, вызванная амио-дароном, встречается часто и требует регулярного мониторинга тиреоидного статуса пациента. Поскольку вмешательство эндокринолога происходит при уже развившейся тиреопатии, перед назначением амиодарона и на фоне его применения необходимо стартовое обследование ЩЖ, которое должно выполняться кардиологом и призвано свести к минимуму риск АмИТ. Классификация АмИТ в большинстве случаев полезна для определения стратегии управления дисфункцией ЩЖ [47]. Кроме того, определение типа АмИТ предсказывает ответ на антитиреоидную терапевтическую стратегию, упрощает принятие решения о продолжении или прекращении приема амиодарона и оценивает прогноз течения АмИТ (рис. 10).
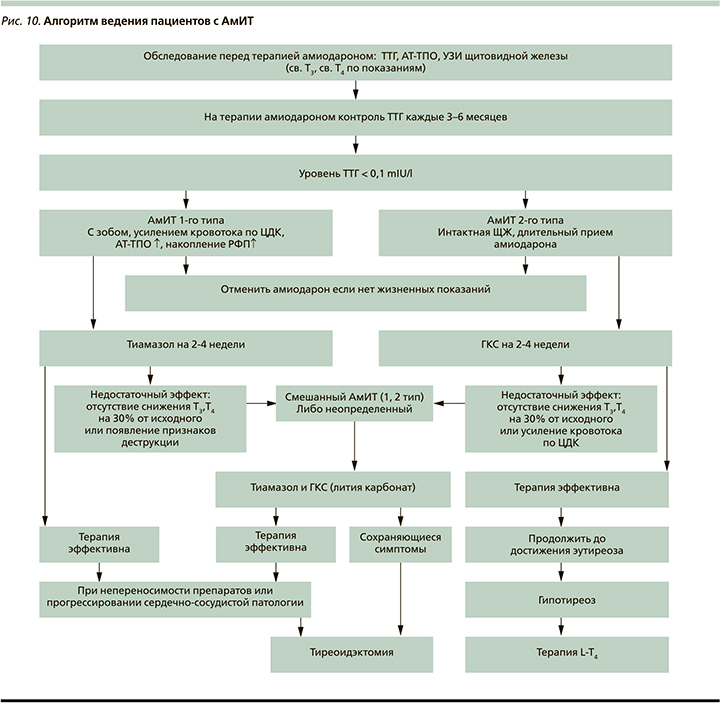
Прием амиодарона можно продолжить или возобновить (в случае прерывания) только у пациентов с АмИТ 2-го типа. Для предотвращения рецидива АмИТ, особенно при высоком риске рецидива АмИТ (в частности, 1-го типа), перед повторным назначением амиодарона рекомендуется провоить абляцию ЩЖ. В случае невозможности отмены или срочности повторного применения амиодарона таким пациентам могут быть предложены низкие дозы тиреостатиков в ожидании операции.



