Введение
Туберкулез – инфекционное заболевание, вызванное Mycobacterium tuberculosis (М. tuberculosis). Согласно отчету ВОЗ, в 2021 г. во всем мире туберкулезом заразились 10 млн человек, причем данное заболевание стало причиной смерти для 1,5 млн [1].
Патогенез туберкулеза начинается с проникновения М. tuberculosis в организм человека. Попав в организм, микобактерия часто закрепляется в тканях легких. На заражение бактерией M. tuberculosis организм отвечает активацией иммунной системы в тканях легких, и первыми вступают в борьбу с инфекцией альвеолярные макрофаги. Макрофаги запускают механизмы активации воспалительных процессов, которые приводят к высвобождению активных форм кислорода и инициации свободно-радикальных процессов. Первичные и вторичные продукты свободно-радикальных реакций обладают выраженной цитотоксичностью [2].
В организме инициаторами свободно-радикального окисления (СРО) также могут служить лекарственные препараты и их токсичные метаболиты, используемые для лечения туберкулеза. В процессе лечения больных лекарственно-чувствительным туберкулезом легких используют противотуберкулезные препараты: изониазид, рифампицин, пиразинамид, этамбутол. Для лечения лекарственно-устойчивого туберкулеза назначаются одновременно пять-шесть противотуберкулезных препаратов c доказанной или предполагаемой лекарственной чувствительностью против возбудителя (капреомицин, пиразинамид, протеонамид, моксифлоксацин/левофлоксацин, бедаквилин, линезолид и др.) [3].
Детоксикация лекарственных средств происходит в две фазы. В первой фазе под действием суперсемейства ферментов цитохрома Р-450 происходит монооксигеназное окисление, которое может приводить к образованию токсичных продуктов, например гидразин и ацетилгидразин (при детоксикации изониазида) [4], деацетилрифампицин (при детоксикации рифампицина) [5], пиразиноевая кислота (при детоксикации пиразинамида) [6], капреомицин (не метаболизируется) [7], сульфоксид протионамида (при детоксикации протионамида) [8], деметиллевофлоксацин и N-оксид левофлоксацин (при детоксикации левофлоксацина) [9], моксифлоксацин (не метаболизируется, неактивные сульфосоединения [М1] и глюкурониды [М2]) [10], гидроксиэтилглицин (при детоксикации линезолида) [11] и т.д. Данные токсичные продукты приводят к усиленной генерации активных форм кислорода, инициации липоперексиных процессов.
Защита тканей клеток от активных форм кислорода и продуктов СРО выполняет антиоксидантная система организма. Чрезмерная активация свободно-радикальных реакций приводит к повреждению клеток, свободные радикалы могут реагировать с липидами клеточной мембраны, вызывая перекисное окисление липидов. Свободные радикалы также могут вызывать окислительную модификацию белков, которые влияют на функции ферментов и других структурных белков [12].
Важнейшим антиоксидантом в организме является глутатион за счет высокой концентрации (внутри клетки 1 до 10 мMоль) и системы ферментов (глутатион пероксидаза, глутатион редуктаза, глутатион трансфераза), которые используют его восстановленную форму для нейтрализации продуктов СРО и обезвреживания токсичных веществ. Кроме того, глутатион регулирует другие жизненно важные процессы в клетке (репарации поврежденной ДНК в ядре; активный транспорт аминокислот; участвует в модуляции иммунного ответа и т.д.) [13, 14].
Цель работы: сравнительная оценка активности СРО липидов в организме больных туберкулезом и здоровых добровольцев.
Методы
Исследование проведено в государственном бюджетном учреждении Республики Саха (Якутия) «Научно-практический центр “Фтизиатрия” им. Е.Н. Андреева» в Якутске. Протокол исследования рассмотрен и одобрен этическим комитетом при ГБУ РС(Я) НПЦ «Фтизиатрия». Все участники исследования подписали информированное согласие.
В исследовании приняли участие 76 пациентов с туберкулезом легких (средний возраст – 42,97+15,38 года), из которых 44 (43,48±8,85 лет) – с лекарственно-чувствительным и 32 (41,48±16,84 года) – с лекарственно-устойчивым туберкулезом. В контрольную группу вошли 40 здоровых добровольцев в возрасте 42,45±11,56 года, по полу и этнической принадлежности соответствовавших группе больных.
Материалом исследования служила венозная кровь, которую брали натощак из локтевой вены. Интенсивность СРО оценивали в сыворотке крови по накоплению концентрации малонового диальдегида при высокой температуре в кислой среде; малоновый диальдегид реагирует с 2-тиобарбитуровой кислотой, образуя окрашенный триметиновый комплекс, согласно протоколу, ранее описанному в работе Costa et al. (2006) [15]. Показатели системы глутатиона были сделаны в гемолизате эритроцитов, приготовленном в соотношении (1:10) в бидистиллированной воде. Концентрацию восстановленного глутатиона оценивали на взаимодействии восстановленного глутатиона с 5,5'-дитио-бис-2-нитробензойной кислотой с образованием окрашенного в желтый цвет аниона 2-нитро-5-тиобензоата по методу Tietze et al. (1969) [16], активности ферментов: глутатион пероксидаза, которая катализирует реакцию взаимодействия восстановленного глутатиона с гидроперекисью трет-бутила, активность фермента при этом может быть оценена по изменению содержания восстановленного глутатиона в пробах до и после инкубации с модельным субстратом в ходе цветной реакции с 5,5'-дитио-бис-2-нитробензойной кислотой по методу Paglia et al. (1967) [17]; глутатион-S-трансфераза, активность которой определяли по скорости образования глутатион-S-коньюгатов между восстановленным глутатионом и 1-хлор-2,4-динитробензолом по методу Habig et al. (1974) [18]; глутатион редуктаза, активность которой определяли по количеству израсходованного в ходе ферментативной реакции кофермента НАДФН по методу Mannervik et al. (1978) [19].
Статистическую обработку проводили с помощью пакета программ SPSS 24 for Windows и Microsoft Excel. Данные статистического анализа представлены в виде средних значений. Значимость различий оценивали с помощью критерия U-критерия Манна–Уитни. Статистически значимыми считали различия при р<0,05.
Результаты и обсуждение
В результате проведенного исследования в крови больных туберкулезом концентрация малонового диальдегида была значимо (в 2,3 раза) выше (р=0,03), а концентрация восстановленного глутатиона ниже в 1,3 раза (р=0,00), чем у здоровых добровольцев (табл. 1).
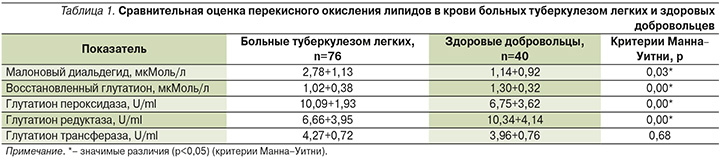
При сравнительном анализе активности ферментов системы глутатиона установлено, что активность глутатион пероксидазы и глутатион трансферазы в крови больных туберкулезом была значимо выше, соответственно в 1,5 (р=0,00) и 1,1 раза (р=0,68), по сравнению с активностью данных ферментов в крови здоровых добровольцев. Установлено значимое снижение активности глутатион редуктазы в 1,5 раза (р=0,00) в крови больных туберкулезом (табл. 1).
При сравнительном анализе активности перекисного окисления липидов в крови среди больных лекарственно-чувствительным туберкулезом, лекарственно-устойчивым туберкулезом и здоровых добровольцев установлено, что в крови больных с различными формами чувствительности микобактерий к противотуберкулезным препаратам концентрации восстановленного глутатиона значимо ниже, чем у здоровых добровольцев. Активность таких ферментов, как глутатион пероксидаза и глутатион редуктаза, в крови больных чувствительными и устойчивыми формами туберкулеза была значимо выше, чем у здоровых добровольцев (табл. 2).
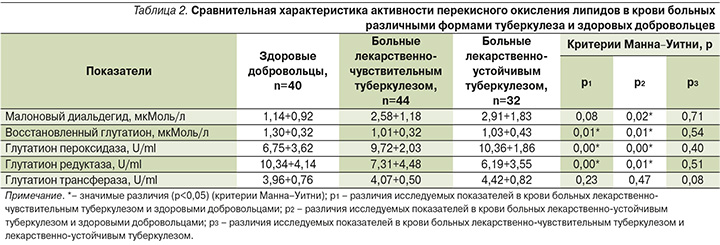
Значимых различий активности СРО липидов в крови больных лекарственно-чувствительным и лекарственно-устойчивым туберкулезом не установлено (табл. 2).
Активные формы кислорода, вырабатываемые организмом в ответ на воздействия M. tuberculosis, приводят к инициации свободнорадикальных реакций [20]. Основная функция глутатиона заключается в обезвреживании активных форм кислорода и продуктов перекисного окисления липидов (перекиси и липоперекиси). Фермент глутатион пероксидаза катализирует восстановление гидроперекисей липидов в соответствующие спирты и восстанавливает пероксид водорода до воды [21]. Кроме антиоксидантной функции глутатион принимает участие в детоксикации лекарственных препаратов и их токсичных метаболитов. Функцию детоксикации осуществляет фермент глутатион трансфераза. Глутатион трансфераза способна катализировать конъюгацию восстановленной формы глутатиона с субстратами ксенобиотиков, превращая их в растворимые в воде менее токсичные вещества [22]. Реакции с участием глутатион пероксидазы и глутатион трансферазы приводят к уменьшению концентрации восстановленной формы глутатиона. Фермент, который восстанавливает окисленную форму глутатиона за счет энергии НАДФ-Н, – глутатион редуктаза [23].
В организме больных туберкулезом отмечено достоверное увеличение интенсификации свободнорадикальных реакций, о чем свидетельствует статистически значимое повышение конечного продукта перекисного окисления липидов – малонового диальдегида (табл. 1).
В ответ на увеличение интенсификации окислительных процессов в организме больных туберкулезом активируется система антиоксидантной защиты. В нашем исследовании достоверно повышается концентрация восстановленной формы глутатиона, а также активности ферментов глутатион пероксидазы и глутатион редуктазы. Активность глутатион трансферазы имела тенденцию к повышению, но изменения значений не достигали уровня статистической значимости (табл. 1). Вероятно, основной причиной снижения концентрации восстановленной формы глутатиона в крови является интенсификация перекисного окисления липидов, а не токсическое действие лекарственных препаратов. Кроме того, истощение уровня восстановленной формы глутатиона у больных туберкулезом усугубляется достоверным снижением в крови активности глутатион редуктазы, чем у здоровых добровольцев.
В исследовании мы предположили, что лекарственно-устойчивый M. tuberculosis может быть связан с системой глутатиона. Но наши результаты показали, что изменения значений концентраций восстановленного глутатиона, а также активности ферментов: глутатион пероксидазы, глутатион редуктазы, глутатион трансферазы, статистически не различались между больными, не имевшими и имевшими лекарственную устойчивость.
Заключение
Таким образом, согласно результатом нашего исследования, можно сделать вывод: в организме больных туберкулезом легких происходит повышение интенсивности СРО на фоне снижения антиоксидантной защиты. Интенсивность СРО липидов и активность системы глутатиона не зависят от лекарственной чувствительности микобактерий, вызвавших туберкулез.



