Введение
В свете стратегии Всемирной организации здравоохранения по ликвидации туберкулеза, декларирующей снижение заболеваемости на 80% до 2030 г., оправданно применение широкого спектра лекарственных препаратов для терапии туберкулеза с множественной, преширокой и широкой лекарственной устойчивостью возбудителя. Лекарственно-устойчивый туберкулез лечат с помощью перепрофилированных препаратов (включая моксифлоксацин, левофлоксацин, линезолид, клофазимин и β-лактамы) и новых лекарств (включая бедаквилин, претоманид и деламанид) [1–3]. Тем не менее изменчивость возбудителя туберкулеза позволяет ему в кратчайшие сроки адаптироваться и формировать устойчивость даже к новым схемам лечения: уже описаны случаи клинической невосприимчивости Mycobactérium tuberculosis к бедаквилину, который считается одним из новейших противотуберкулезных препаратов (ПТП) [4]. В связи c этим актуальной представляется разработка нового отечественного ПТП из группы диарилхинолинов с рабочим названием тиозонид (АО «Фарм-Синтез»). Лекарственное средство по химической структуре представляет собой (1R,2S+1S,2R)-1-(6-Бром-2-хлорхинолил-3-ил)-4-(диметиламино)-2-(нафталин-1-ил)-1-фенилбутан-2-ол [5]. Этот препарат обладает специфической противотуберкулезной активностью как в исследованиях in vitro, так и in vivo в экспериментальных исследованиях на животных. На модели генерализованного туберкулеза у мышей было показано, что показатели КОЕ микобактерии туберкулеза в легких мышей при монотерапии тиозонидом сравнимы с таковыми при монотерапии рифампицином в аналогичной дозе. Показано также, что имеет место синергизм с противотуберкулезными препаратами 1-го ряда изониазидом, рифампицином и этамбутолом, в частности совместная терапия тиозонидом с изониазидом или рифампицином приводит практически к полному выздоровлению подопытных животных, что доказано бактериологически и гистологически [6].
Целью настоящего исследования была оценка эффективности препарата тиозонид, включенного в комплексную схему лечения пациентов с диагнозом «туберкулез легких» с множественной или широкой лекарственной устойчивостью микобактерии туберкулеза (МЛУ-ТБ или ШЛУ-ТБ).
Методы
Оценка безопасности и эффективности применения тиозонида у пациентов с диагнозом МЛУ-ТБ или ШЛУ-ТБ, находившихся на стационарном или амбулаторном лечении в рамках многоцентрового клинического исследования «Многоцентровое 12-недельное двойное слепое рандомизированное, плацебо-контролируемое клиническое исследование по подбору оптимальных дозировок лекарственного препарата тиозонид, капсулы (ЗАО «Фарм-Синтез»), на фоне стандартной противотуберкулезной химиотерапии (ХТ) у пациентов с диагнозом туберкулеза легких с множественной или широкой лекарственной устойчивостью микобактерий туберкулеза» (Разрешение на клиническое исследование Министерства здравоохранения Российской Федерации № 661 от 24.11.2014). В исследование были включены 160 человек и на визите скрининга рандомизированы в одну их четырех групп (в соотношении 1:1:1:1). Все группы получали исследуемый препарат/плацебо 1 раз в сутки. Во избежание раздражения пищевода пациенты принимали капсулы, запивая 200 мл кипяченой воды комнатной температуры, стоя или сидя в прямом положении вне зависимости от приема пищи. Согласно инструкции, пациенты принимали капсулы целиком, не ломая или разжевывая.
Группа I получала исследуемый препарат тиозонид в дозе 200 мг (2 капсулы с исследуемым препаратом и 4 капсулы с плацебо)+стандартная противотуберкулезная ХТ; группа II получала исследуемый препарат тиозонид в дозе 400 мг (4 капсулы с исследуемым препаратом и 2 капсулы с плацебо)+стандартная противотуберкулезная ХТ; группа III получала исследуемый препарат тиозонид в дозе 600 мг (6 капсул с исследуемым препаратом)+стандартная противотуберкулезная ХТ; группа IV получала 6 капсул плацебо+стандартная противотуберкулезная ХТ.
В качестве стандартной противотуберкулезной ХТ для пациентов с диагнозом «туберкулез легких с множественной лекарственной устойчивостью» (согласно Приказу МЗ РФ № 109 от 21.03.2003, Приложение 6, и Федеральным клиническим рекомендациям по диагностике и лечению туберкулеза органов дыхания с множественной и широкой лекарственной устойчивостью возбудителя, издание второе [2014]) использовались препараты IV режима ХТ: комбинация как минимум из 5 противотуберкулезных препаратов, чувствительность к которым сохранена, например, пиразинамид, препарат из группы фторхинолонов (например, левофлоксацин или моксифлоксацин), канамицин/амикацин или капреомицин, протионамид/этионамид или ПАСК, этамбутол, циклосерин или теризидон. Для пациентов с диагнозом «туберкулез легких с широкой лекарственной устойчивостью» использовались препараты V режима, состоявшего как минимум из 6 противотуберкулезных препаратов, чувствительность к которым сохранена: капреомицин/амикацин или канамицин, препарат из группы фторхинолонов (например, левофлоксацин или моксифлоксацин), пиразинамид, этамбутол, циклосерин/теризидон, протионамид/этионамид, ПАСК, линезолид. Назначение препаратов резервного ряда зависит от данных исследования лекарственной чувствительности выделяемых больным микобактерий туберкулеза (МБТ), причем учитываются данные о лекарственной устойчивости микобактерий по региону.
В соответствии с утвержденным Минздравом РФ протоколом клинических исследований 2-й фазы в качестве основного критерия эффективности комбинированного лечения больных туберкулезом с МЛУ и ШЛУ с применением различных доз препарата тиозонид по сравнению с применением плацебо оценивали следующие первичные конечные точки (ПКТ):
- динамика количественного содержания МБТ в мокроте пациентов, определяемого бактериоскопическим методом светодиодной люминесцентной микроскопии с использованием окраски по Цилю-Нильсену на визитах 5–10 (дни исследования – лечения: 14, 28, 42, 56, 70 и 84 соответственно) по сравнению с данными, полученными на визите скрининга;
- динамика количественного содержания МБТ, определяемого путем оценки колониеобразующих единиц (КОЕ) микобактерий в мокроте пациентов бактериологическим методом посева на жидких питательных средах (автоматизированная система BACTEC) на визитах 6, 8 и 10 (дни исследования – лечения: 28, 56 и 84 соответственно) по сравнению с данными, полученными на визите скрининга.
Достижением терапевтической эффективности считалось выявление статистически значимых различий на визите окончания лечения или на предшествовавшем визите/визитах с их сохранением до конца лечения для обеих ПКТ.
Для обеспечения возможности выполнения стандартизированного статистического анализа достоверности достижения ПКТ количественные показатели МБТ, определяемые бактериоскопически и характеризующиеся высоким разбросом, были нормированы путем перевода количества выявляемых кислотоустойчивых микобактерий (КУМ) в баллы по представленной схеме:
- КУМ не обнаружены в 300 п/з – отрицательный результат (0 баллов);
- 1–9 КУМ в 100 п/з – положительный результат (1 балл);
- 10–99 КУМ в 100 п/з – положительный результат (2 балла);
- 1–10 КУМ в 1 п/з – положительный результат (3 балла);
- более 10 КУМ в 1 п/з – положительный результат (4 балла).
Оценка числа МБТ в мокроте по данным посева проводилась на скрининге, а также на визитах 6, 8 и 10. Для стандартизации количественные показатели МБТ, определяемые бактериологически и характеризующиеся высоким разбросом, были нормированы путем перевода числа колониеобразующих единиц (КОЕ) в баллы по представленной схеме:
- отсутствие роста МБТ – отрицательный результат (0 баллов);
- 1–20 КОЕ – «скудное» бактериовыделение, положительный результат (1 балл);
- 21–100 КОЕ – «умеренное» бактерио-выделение, положительный результат (2 балла);
- >100 КОЕ – «обильное» бактериовыделение, положительный результат (3 балла);
Полученные данные подвергались статистической обработке с помощью программы Statistica 6.0 for Windows. Количественные показатели в виде М±SЕ, где М – среднее значение, а SЕ – стандартная ошибка среднего. Для проверки различий качественных показателей использовали непараметрический критерий Манна–Уитни (попарные сравнения несвязанных совокупностей данных), если достигнутый уровень значимости различий не превышал 0,05, их считали достоверными [7].
Результаты
Эффективность применения оценивали по балльной шкале бактериоскопии, в табл. 1 приведена динамика этих показателей (разница между показателями на визитах 7–10 и на скрининге) в группах приема тиозонида (400 и 600 мг) по сравнению с группой плацебо.
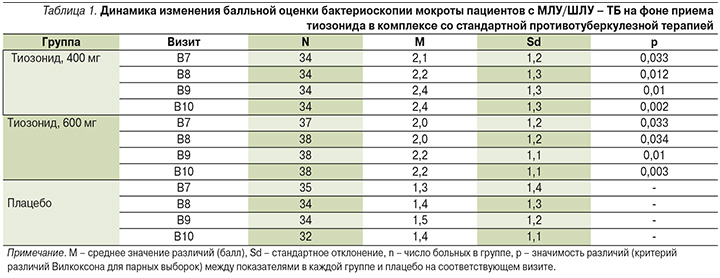
В соответствии с условиями достижения ПКТ статистический анализ с оценкой достоверности различий проведен попарно между средними показателями в группах приема тиозонида и в группе приема плацебо. В табл. 1 представлены показатели групп 2 и 3 на визитах 7–10, для которых были выявлены достоверные различия с группой 4 (плацебо). Общий характер изменений показателей бактериоскопии для 1–4-й групп на визитах 5–10 исследования представлен на рис. 1.

Анализ результатов исследований, приведенных в табл. 1, показал существенный рост темпа снижения показателей бактериоскопии мокроты пациентов в процессе продолжительного лечения в группах приема тиозонида. Это снижение было наиболее выражено в группе 2 (400 мг) и составило 2,4 балла, или 93%, на 10-м визите (84-й день лечения) по сравнению со значением до лечения, равным 2,6 балла. Лечение в этой группе привело к отсутствию МБТ в мокроте у большинства больных. С другой стороны, снижение показателя бактериоскопии мокроты на 10-м визите в группе 4 (плацебо) было существенно менее выраженным и составило 1,4 балла, или 42%, по сравнению со значением до лечения, равным 2,4 балла.
Полученные результаты показали, что применение тиозонида в дозах 400 и 600 мг обеспечило достижение первого критерия комплексной ПКТ по сравнению с плацебо: отрицательной динамики содержания МБТ в мокроте, измеренного методом бактериоскопии.
Следовательно, при использовании этих двух дозировок тиозонида динамика снижения числа МБТ в мокроте достоверно отличалась от показателей динамики при использовании плацебо уже на 7-м визите (42-й день терапии), и эти различия сохранялись на последующих визитах вплоть до окончания лечения (84-й день).

В табл. 2 приведена динамика показателей бактериологических исследований в баллах (разница между показателями на визитах 8, 10 и на скрининге) в группах приема тиозонида (400 и 600 мг) по сравнению с группой 4 (плацебо). В табл. 2 представлены показатели групп 2 и 3 на визитах 8–10, для которых были выявлены достоверные различия с группой 4 (плацебо). Общий характер изменений показателей бактериологических исследований для 1–4-й групп на визитах 6, 8 и 10 представлен на рис. 2. В соответствии с условиями достижения ПКТ статистический анализ с оценкой достоверности различий проведен попарно между средними показателями в группах приема тиозонида и в группе приема плацебо.
Анализ результатов исследований, приведенных в табл. 2, как и при бактериоскопии мокроты, показал существенный рост темпа снижения показателей бактериологического исследования у пациентов, принимавших тиозонид. Это снижение было наиболее выраженным в группе приема 400 мг препарата и составило 2 балла, или 95%, на последнем, 10-м, визите по сравнению со значением до лечения, равным 2,1 балла. То есть лечение в этой группе привело к отсутствию МБТ в мокроте у большинства больных.
С другой стороны, снижение показателя бактериологического исследования мокроты на 10-м визите у пациентов, принимавших плацебо, было менее выраженным и составило 1,1 балла, или 56%, по сравнению со значением до лечения, равным 1,9 балла.
Полученные результаты продемонстрировали, что применение тиозонида в дозах 400 и 600 мг обеспечило достижение второго критерия комплексной ПКТ по сравнению с плацебо. Показано, что при использовании этих 2 доз тиозонида динамика снижения числа МБТ в мокроте достоверно отличалась от показателей динамики при использовании плацебо на 56-й и 84-й дни лечения.
Таким образом, в проведенном исследовании доказано достижение комплексной ПКТ в соответствии с протоколом 2-й фазы клинического исследования, что позволяет сделать вывод об эффективности применения препарата тиозонид (в дозировках 400 и 600 мг) в комбинированной терапии больных туберкулезом с МЛУ и ШЛУ.
Обсуждение
Препараты группы диарилхинолинов считаются одними из оптимальных кандидатных молекул для лечения МЛУ-ТБ. Согласно данным, наиболее вероятной мишенью с карманом связывания тиозонида является субъединица бактериальной АТФ-синтазы – фермента, играющего ключевую роль в процессах энергообмена клетки за счет сопряжения реакции синтеза/гидролиза АТФ с трансмембранным переносом протонов [8, 9]. Основной проблемой существующих на сегодняшний день ПТП, используемых для лечения туберкулеза МЛУ- и ШЛУ-ТБ, являются устойчивость к ним возбудителя, а также неудовлетворительный профиль побочных эффектов. В отношении препаратов группы диарилхинолинов, к которым относится зарегистрированный в настоящее время первый в этом классе ПТП бедаквилин, можно говорить о хорошем профиле переносимости пациентами и уникальном специфическом механизме действия на M. tuberculosis [10].
Для ПТП характерна дозозависомость эффектов, причем как в эксперименте [11, 12], так и в клинической практике. Это касается не только побочных эффектов [13], но и показателей эффективности, как в настоящем исследовании, показавшем определенную дозозависимость эффективности препарата тиозонид. Доза 200 мг демонстрировала тенденцию к эффективности, хотя статистически достоверная разница отмечалась только 1 раз (при бактериоскопии на 10-м визите). В то же время существенной разницы между дозами 400 и 600 мг в результатах (бактериоскопических и бактериологических) не было выявлено, из чего можно сделать предположение, что «плато» эффективности было достигнуто и повышение дозы не приводило к изменениям показателей эффективности препарата.
Заключение
Результаты изучения эффективности препарата тиозонид в комплексной терапии пациентов с МЛУ- и ШЛУ-ТБ продемонстрировали, что применение тиозонида в дозах 400 и 600 мг обеспечивало достижение комплексной первичной конечной точки по сравнению с плацебо в отношении динамики содержания МБТ в мокроте, измеренной бактериоскопическим и бактериологическим методами. Полученные данные позволяют обосновать размер выборки и режим терапии для исследования третьей фазы препарата тиозонид.



