Введение
Острый психотический эпизод – состояние, которое проявляется в виде бреда, галлюцинаций, спутанности сознания и аффективной неустойчивости [1]. Доказано, что антипсихотики облегчают психотические симптомы, предотвращают их рецидивы [2, 3]. Антипсихотики второго поколения в отличие от антипсихотиков первого поколения реже вызывают экстрапирамидные расстройства и чаще ассоциированы с метаболическими расстройствами, такими как дислипидемия, увеличение веса и сахарный диабет 2 типа [4].
Галоперидол – антипсихотик первого поколения. Его открытие в 1958 г. стало одним из величайших достижений психиатрии XX в. [5].
Галоперидол – одно из наиболее изученных и часто используемых средств лечения шизофрении, доступное в различных формах [6]. Хотя галоперидол – «старое» лекарство, его доступность в разных формах введения и высокая потентность объясняют частое применение [5]. Галоперидол довольно эффективен, в т.ч. у детей при лечении расстройств шизофренического спектра. Однако применение галоперидола может ассоциироваться с нежелательными реакциями [7]. Выраженность нежелательных реакций и эффективность галоперидола индивидуальны для каждого конкретного пациента. Выявление фармакокинетических и фармакодинамических факторов, лежащих в основе индивидуальной восприимчивости препарата, является задачей персонализированной медицины.
Прогнозирование эффективности и безопасности антипсихотиков на основе результатов фармакогенетического тестирования в настоящее время активно изучается [8]. Согласно исследованиям последних десятилетий, генетические полиморфизмы способны прогнозировать клинический ответ на терапию или нежелательные реакции, вызванные лекарственными препаратами [9]. Наиболее перспективными являются фармакокинетические генетические факторы, в частности гены изоферментов цитохрома P-450 (СYP). Для антипсихотиков наиболее актуально генотипирование CYP2D6 [10]. Cубстратами CYP2D6 являются более 70 лекарственных препаратов, в т.ч. и галоперидол.
Еще одним важным фармакокинетическим фактором служит транспортный белок P-гликопротеин (P-gp), кодируемый геном ABCB1. P-gp – эффлюксный транспортер, создающий барьер для ксенобиотиков. Большая активность P-gp ассоциирована с уменьшением биодоступности его субстратов, к таковым относятся многие лекарственный препараты [4].
Активность P-gp генетически детерминирована, определенные полиморфные варианты гена ABCB1 ассоциированы со снижением активности транспортера [11]. Но конкретно в отношении влияния ABCB1 на эффективность и безопасность галоперидола данные исследований противоречивы [12].
Галоперидол – конкурентный антагонист постсинаптических D2-рецепторов в головном мозге, а также антагонист 5-HT2-рецепторов [13]. Рецепторы дофамина D2 кодируются геном DRD2. Наличие полиморфных вариантов в гене DRD2 может приводить к изменению плотности рецепторов дофамина 2-го типа в стриатуме [14, 15]. Известно, что полиморфизм Taq1A (rs1800497; g.32806C>T) гена DRD2 снижает плотность рецепторов D2 полосатого тела и, вероятно, изменяет их аффинность к галоперидолу [13].
Продемонстрировано прогностическое значение полиморфного варианта CYP2D6*4 для переносимости галоперидола в одном из исследований [19].
Изучение фармакогенетических предикторов его эффективности и безопасности для подростков актуально, поскольку многие антипсихотики второго поколения не разрешены к применению до 18 лет [20, 21].
Цель исследования: выявление фармакогенетических предикторов нежелательных реакций и неэффективности галоперидола у подростков с острым психотическим эпизодом.
Методы
Дизайн исследования
Исследование одобрено заседанием локального этического комитета ФГБОУ ДПО РМАНПО «Российской медицинской академией непрерывного профессионального образования» Минздрава России (Протокол № 3 от 06.06.2018) и ГБУЗ «Научно-практический центр психического здоровья детей и подростков им. Г.Е. Сухаревой» ДЗМ (Протокол № 2 от 14.06.2018).
Дизайн исследования: проспективное обсервационное исследование ассоциации фармакогенетических факторов с параметрами безопасности галоперидола для подростков с острым психотическим эпизодом.
В исследовании участвовали пациенты, госпитализированные в детскую психиатрическую больницу (ГБУЗ «Научно-практический центр психического здоровья детей и подростков им. Г.Е. Сухаревой» ДЗМ).
В исследовании участвовали пациенты, госпитализированные в больницу с 20.06.2018 по 20.03.2020.
Выборка
В исследование были включены 56 подростков с установленным диагнозом «острое полиморфное психотическое расстройство» на момент поступления (F23.0-9, согласно МКБ-10). Включение производилось в срок от 1 до 3 дней после госпитализации пациента в психиатрическую больницу. Каждый пациент или его законный представитель подписал добровольное информированное согласие на участие в исследовании. Персональные данные, которые позволяют идентифицировать пациента, не были внесены в базы данных. Все пациенты идентифицировали себя этнически русскими.
Критерии включения:
1. Возраст от 10 до 18 лет;
2. Клинически верифицированный острый психотический эпизод;
3. Назначение галоперидола в качестве основного вида фармакотерапии;
4. Согласие пациента и родителя (законного представителя) на участие в исследовании.
Критерии невключения:
1. Наличие соматического или инфекционного заболевания в состоянии декомпенсации;
2. Положительный результат теста на употребление психоактивных веществ, что указывает на экзогенный характер психотического расстройства;
3. Противопоказания к приему антипсихотиков;
4. Отказ пациента или его родителя (законного представителя) от участия в исследовании.
Наблюдение за пациентами проводилось в течение 14 дней. Безопасность психофармакотерапии оценивалась на 14-й день наблюдения.
Оценка безопасности фармакотерапии
Безопасность психофармакотерапии оценивалась при помощи шкал UKU Side Effects Rating Scale (UKU SERS), Sympson-Angus Scale (SAS), Barnes Akathisia rating scale (BARS) [22]. Эти шкалы имеют числовые значения: чем выше значение, тем больше выраженность симптомов. Но UKU SERS также позволяет оценивать наличие отдельных неблагоприятных реакций у пациента. Кроме того, шкала UKU SERS включает подшкалы: нарушения со стороны психики, неврологические нарушения, нарушения вегетативной нервной системы.
Исследователь не мог влиять на назначение психофармакотерапии лечащим врачом. Все получаемые пациентом психотропные препараты были учтены в исследовании. Все пациенты получали галоперидол в качестве основной терапии. Некоторым пациентам дополнительно назначали второй антипсихотик, антидепрессант, нормотимик, антихолинергический препарат или транквилизатор. Подобные случаи рассматривались как полипрагмазия и обязательно учитывались при анализе. Для анализа учитывали суточную дозу галоперидола, не разделяя по пути введения. В анализ включались только те лекарственные средства, которые назначались пациенту не менее чем на 3 дня.
Лабораторная часть
От каждого пациента был взят соскоб эпителия внутренней стороны щеки (буккального эпителия) в день включения в исследование с целью генотипирования. Биоматериал замораживался, транспортировался в лабораторию и в дальнейшем хранился при температуре -77°С.
Лабораторная часть исследования проводилась на базе НИИ молекулярной и персонализированной медицины ФГБОУ ДПО РМАНПО Минздрава России (Москва). Выделение ДНК и генотипирование образцов происходили по мере их поступления в период с 25 апреля 2019 по 15 мая 2020 г.
Выделение ДНК из буккального эпителия проведено сорбентным методом.
Полиморфные варианты генов CYP3A4*22 (rs2740574), CYP3A5*3 (6986A>G, rs7776746), CYP2D6*4,*9,*10 (rs3892097, rs1065852), ABCB1 1236C>T (rs1128503), 2677G>T/A (rs2032582), 3435C>T (rs1045642), COMT rs4680 (G>A – Val158Met), DRD3 rs6280 (C>T), DRD3 rs324026 (C>T), HTR2A rs6313 (T102C), ZNF804A rs1344706 (G>T), HTR2A rs6313 (T102C), ANKS1B rs7968606 (C>T) были определены методом полимеразной цепной реакции (ПЦР) в реальном времени с применением коммерческих наборов реактивов (ООО «Синтол»), оборудование: детектирующий амплификатор CFX96 TouchTM Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad, USA)
Статистическая обработка результатов
Статистическая обработка проводилась в программе SPSS Statistics 21.0. С учетом небольшего размера выборки для сравнения количественных переменных между группами применялись непараметрические критерии (Манна–Уитни, Крускала–Уоллеса). Ввиду малочисленной выборки средние значения в результатах представлены как медиана и квартили – Me [Q1; Q3]. Частоты категориальных переменных сравнивались между собой при помощи Хи-квадрата Пирсона, для сравнений 2×2 использовался точный критерий Фишера. Для коррекции множественных сравнений вводилась поправка Бонферрони. Расчет соответствия распределения генотипов закону Харди–Вайнберга выполнен при помощи онлайн-калькулятора. Носители разных аллелей полиморфных вариантов были разбиты на две группы: носители «дикой» аллели в гомозиготном состоянии (TT) и носители полиморфной аллели (CС+СТ). Такое разбиение было применено в связи с численностью пациентов с разными генотипами для формирования подходящих для статистического анализа подгрупп. При анализе данных всегда учитывалось влияние демографических и клинических характеристик пациентов на изучаемые исходы, в т.ч. влияние полипрагмазии. Это было сделано с целью установить значимость ассоциаций полиморфных вариантов исследуемых генов с параметрами эффективности и безопасности антипсихотиков.
Результаты
Общая характеристика пациентов, включенных в исследование, представлена в табл. 1.
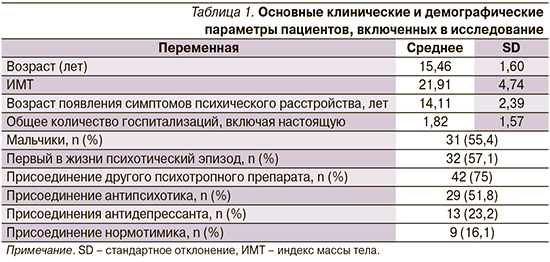
Хотя основным препаратом для 56 подростков был галоперидол, в 75% случаев наблюдалось присоединение дополнительного психотропного препарата.
Проверка выборки на соответствие равновесию Харди–Вайнберга установила, что частоты полиморфных вариантов CYP3A5*3, DRD3 rs6280, DRD3 rs324026, DRD4 rs1800955 и HTR2A rs6313 значимо отличаются от ожидаемых.
Было проведено сравнение клинических и демографических параметров между носителями разных генотипов полиморфных вариантов для определения их сопоставимости.
В результате не выявлено статистически значимых ассоциаций между клинико-демографическими показателями и носительством полиморфизмов.
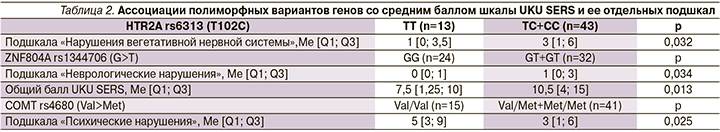
Ниже представлены значимые ассоциации параметров безопасности фармакотерапии с изученными полиморфными вариантами.
Ассоциации полиморфных вариантов исследуемых генов с параметрами безопасности фармакотерапии
Установлены значимые ассоциации между полиморфными вариантами COMT rs4680, HTR2A rs6313, ZNF804A rs1344706 и выраженностью нежелательных реакций у пациентов. Как продемонстрировано в табл. 2, носительство полиморфного варианта COMT rs4680 (аллель Met) ассоциировалось с меньшей выраженностью нежелательных реакций со стороны психики. Для полиморфизмов HTR2A rs6313 и ZNF804A rs1344706 наблюдается обратная закономерность: их наличие у пациента значимо ассоциировано с большим баллом шкалы UKU SERS.
Проведен анализ частоты встречаемости конкретных нежелательных реакций (НР) в зависимости от носительства полиморфных вариантов исследованных генов.
Носители полиморфного варианта HTR2A rs6313 (генотипы TC+CC) чаще жаловались на развитие тремора (37,2 против 0%, p=0,009).
Носительство ABCB1 1236C>T и 2677G>T/A чаще ассоциировалось с наличием ортостатического головокружения по сравнению с гомозиготами «дикого» типа (35 против 6,3%, p=0,028, ввиду неравновесного сцепления данные совпадают для обоих полиморфных вариантов).
Частота развития ортостатического головокружения также была значимо выше у носителей полиморфизма ZNF804A rs1344706 по сравнению с гомозиготами GG (37,5 против 12,5%; p=0,037).
Носительство полиморфных вариантов DRD3 rs6280 и rs324026 значимо ассоциировалось с урежением такой НР, как «увеличение интенсивности сновидений». При гомозиготном носительстве DRD3 rs6280 частота НР составляла 7,1% (у носителей CC+СT=50,1%; p=0,004), для rs324026 – 17,4% (у носителей CC+CT=54,5%; p=0,005).
Обсуждение результатов
Установлены значимые отличия частоты нежелательных реакций и баллов подшкал UKU между носителями полиморфных вариантов COMT rs4680, DRD3 rs6280, HTR2A rs6313, ZNF804A rs1344706.
Данное исследование показало, что носительство полиморфного варианта COMT rs4680 (Vall58Met) ассоциировано с лучшей переносимостью терапии, согласно шкале UKU SERS. СОМТ – ген, кодирующий катехол-О-метилтрансферазу, участвующую в элиминации дофамина, а также разрушении его в синаптической щели. Полиморфизм COMT rs4680 (Val158Met) кодирует замену аминокислоты валина (Val) на метионин (Met) в кодоне 158. Согласно исследованиям, присутствие аллеля Met снижает активность COMT на 25% по сравнению с активностью Val-содержащего фермента. Это приводит к более высоким концентрациям синаптического дофамина у носителей Met-аллеля за счет меньшей деградации его в синаптической щели. В нашем исследовании носительство аллеля Met ассоциировалось с меньшей выраженностью НР со стороны психики. По шкале UKU SERS, в эту категорию входят снижение концентрации внимания, седация, сонливость, раздражительность, нарушения сна и т.д. Можно предположить, что меньшая активность COMT в синаптической щели смягчала антидофаминергическое действие антипсихотиков. Посредством этого НР со стороны психики были менее чувствительны для пациента.
Мы выявили, что носительство полиморфизма DRD3 rs6280 (A>C) реже ассоциировано с увеличением интенсивности сновидений по сравнению с «диким» генотипом AA. Носительство полиморфизма DRD3 rs6280 приводит к снижению аффинности рецептора к дофамину [23]. Считается, что единственным нейромедиатором, функционирующим в REM-фазу сна, является дофамин. Выявлена связь между концентрацией дофамина и увеличением частоты продолжительности, но не интенсивности сновидений. Однако есть предположение, что отсутствие активности других моноаминов во время фазы парадоксального сна усиливает действие дофамина на кору больших полушарий [24].
В 2002 г. представлены доказательства того, что физиологическая регуляция активности дофаминовых нейронов связана с серотониновыми рецепторами 5-HTR2A, расположенными на дофаминовых нейронах вентральной области покрышки [27]. Было показано, что стимуляция кортикальных 5-HTR2A рецепторов ведет к увеличению выработки дофамина и ослаблению действия галоперидола. В частности, выявлено, что наличие аллели HTR2A 102C связано со сниженной экспрессией гена, что предположительно ведет к ригидности серотонинергической системы, соответственно, к уменьшению дофаминергической модуляции и плохому ответу на галоперидол [28, 29]. Это подтверждают полученные нами результаты, в которых носительство полиморфизма HTR2A rs6313 (T102C) было чаще ассоциировано с тремором и увеличением среднего балла подшкалы UKU «Нарушения вегетативной нервной системы».
Ген ZNF804A кодирует цинк-пальцевой белок, участвующий в развитии нервной системы [28]. Точные биологические функции ZNF804A, лежащие в основе его связи с мозгом, остаются активной областью исследований. Однако в недавних исследованиях выявлено, что носительство полиморфизма ZNF804A rs1344706 (G>T) является маркером тяжести течения шизофрении и резистентности к психофармакотерапии [14]. В нашем исследовании найдены значимые ассоциации между носительством полиморфизма ZNF804A rs1344706 (G>T) и увеличением среднего балла подшкалы UKU «Неврологические нарушения» и общего балла UKU.
Ограничения
Ограничениями настоящего исследования служат небольшая выборка пациентов, а также применение сопутствующей психофармакотерапии. Цель исследования – установить генетические факторы риска развития НР на прием галоперидола. Поскольку большинство пациентов принимали другие психотропные препараты, в т.ч. антипсихотики, есть ограничения при интерпретации результатов исследования. Но основным антипсихотиком, назначенным для терапии острого психотического эпизода, являлся галоперидол. Следовательно, его вклад как в эффективность, так и в безопасность фармакотерапии можно считать основным.
Заключение
В результате проведенного исследования выявлены полиморфные варианты генов, ассоциированные с безопасностью психофармакотерапии с использованием галоперидола у подростков с острым психотическим эпизодом.
Увеличение риска нежелательных реакций наблюдалось при носительстве полиморфных вариантов HTR2A rs6313 (генотипы TC+CC), ABCB1 1236C>T и 2677G>T/A, ZNF804A rs1344706. Установлено, что носительство COMT rs4680 (аллель Met), DRD3 rs6280 и rs324026 ассоциировалось с меньшей выраженностью нежелательных реакций по сравнению с «дикими» генотипами.
Галоперидол является высокопотентным антипсихотиком первой генерации, его применение для купирования острого психотического эпизода целесообразно. Но проведение фармакогенетических исследований необходимо, чтобы выявлять группы риска среди пациентов. В случае наличия генетической предрасположенности к НР следует начинать фармакотерапию острого психотического эпизода с антипсихотика второй генерации. Для разработки диагностического алгоритма требуется проведение новых фармакогенетических исследований среди данного контингента пациентов.
Финансирование. Исследование выполнено при финансовой поддержке Российского научного фонда, проект № 18-75-00046.



