Введение
Сахарный диабет (СД) – одно из наиболее распространенных заболеваний XXI в. В мире 537 млн человек в возрасте 20–79 лет страдают СД, при этом 90% всех случаев приходится на СД 2 типа (СД2) [1]. В Российской Федерации (РФ) отмечается значимый рост распространенности СД. По данным Московского сегмента Федерального регистра, общая численность пациентов с СД в Москве, состоящих на диспансерном учете, на 01.01.2023 составила 353 346 [2]. Важно отметить, что затраты на лечение пациентов, у которых развились микро- и макрососудистые осложнения СД, превосходят затраты на лечение пациентов без осложнений, в случае СД2 – в 3 раза [4]. Пациенты с СД имеют двукратное увеличение риска развития сердечно-сосудистых заболеваний (ССЗ) [5]. В 2021 г. в мире умерли 6,7 млн пациентов в возрасте 20–79 лет от СД и его осложнений [1].
Самоконтроль СД
Важной опцией эффективной терапии СД является самостоятельный контроль показателей гликемии пациентом в домашних условиях. Самоконтроль способствует достижению и длительному удержанию показателей углеводного обмена в целевом диапазоне и является важнейшим фактором, позволяющим снижать риск развития поздних осложнений СД.
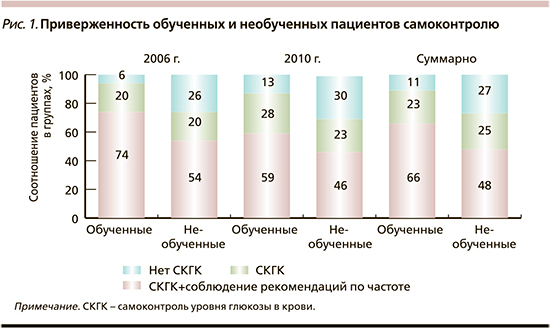
Несмотря на использование широкого спектра современных сахароснижающих препаратов для лечения СД, большинство больных не достигают целевых показателей гликемического контроля. В настоящее время средства самоконтроля доступны больныv СД, однако приверженность проведению самоконтроля остается низкой. Только 44% взрослых с СД1 и 24% больных СД2 проводят регулярный самоконтроль в соответствии с рекомендацией врача. У молодых пациентов приверженность самоконтролю составляет 31–69%. Она выше у обученных пациентов. Без данных самоконтроля невозможно проведение коррекции сахароснижающей терапии. Это является одной из основных причин того, что пациенты не достигают целей терапии [6, 7] (рис. 1).
Оценка уровня гликированного гемоглобина (HbA1c) остается «золотым» стандартом эффективности проводимой терапии больных СД. В Российских алгоритмах специализированной медицинской помощи больным сахарным диабетом (10-й выпуск, 2022) выбор целевого уровня HbA1c зависит от возраста пациента, ожидаемой продолжительности жизни, наличия тяжелых макрососудистых осложнений и риска тяжелой гипогликемии (табл. 1).
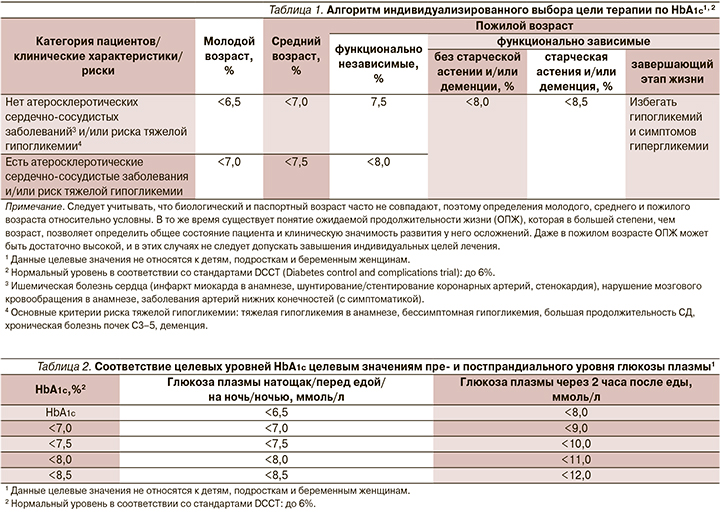
Больным СД рекомендуются индивидуальные цели лечения не только по уровню НbА1с, но и по гликемии натощак (ГПН), постпрандиальной гликемии. Целевые уровни глюкозы плазмы натощак/перед едой/на ночь/ночью по значению совпадают с целевым уровнем HbA1c. Глюкоза плазмы через 2 часа от начала приема пищи соответствует уровню менее 8 ммоль/л при HbA1c менее 6,5%, а далее увеличивается на 1 ммоль/л на каждые 0,5% HbA1c (табл. 2) [8].
В 2013 г. Международная диабетическая федерация предложила увеличение целевого уровня HbA1c до 8,5% у пациентов пожилого возраста, имеющих деменцию или физически ослабленных, которые не могут самостоятельно себя обслуживать.
Каждого пациента необходимо проинформировать о его индивидуальном целевом уровне НbА1с, ГПН/перед едой/на ночь/ночью и глюкозы плазмы через 2 часа после начала приема пищи для того, чтобы он знал, к чему надо стремиться [8].
В течение многих лет подходы к терапии СД основывались на понимании связи между HbA1c и отдаленными исходами данного заболевания вне зависимости от его типа. В классических исследованиях среди популяции пациентов СД1 (DCCT) и СД2 (UKPDS – UK Prospective Diabetes Study) продемонстрировано: снижение уровня HbA1c ассоциировано с клинически значимым снижением риска развития микрососудистых осложнений и ССЗ [9, 10]. Между тем уровень HbA1c является средним интегральным показателем уровня глюкозы крови за 3 прошедших месяца и не учитывает амплитуды и частоты колебаний гликемии. Таким образом, уровень HbA1c не отражает таких важных аспектов, как вариабельность гликемии в течение дня и изо дня в день, а также частоту гипогликемических состояний. Это означает, что достижение цели по уровню НbА1с далеко не в каждой клинической ситуации свидетельствует об эффективности и безопасности проводимой сахароснижающей терапии. Поэтому недостаточно опираться только на уровень HbA1c, т.к., руководствуясь только им, ни пациент, ни врач не могут достоверно оценить, в какой период времени значения гликемии были выше верхней границы целевого уровня, а в какой – ниже нижней границы.
Недостижение целевого уровеня НbА1с свидетельствует о необходимости изменения дозы препаратов или схемы терапии. Коррекцию дозы инсулина и сахароснижающих препаратов врач проводит на основании показателей гликемии, которые пациент предоставляет ему на визите. В свою очередь, зная результаты самоконтроля, врач предоставляет пациенту рекомендации по питанию, физической активности, коррекции терапии.
Мониторинг гликемии
В лечении СД огромную роль играет эффективное взаимодействие между врачом и пациентом, позволяющее достигать индивидуальных целевых показателей гликемии. Большое значение в достижении целей терапии имеют знания и навыки, благодаря которым пациент может управлять своим заболеванием, а также достаточный уровень мотивации к их использованию. В работу врача входит не только проведение обследования и подбор терапии, но и осуществление процесса обучения и мотивации пациента на достижение целей терапии. Особое место в концепции лечения СД отводится повышению качества жизни пациентов, адаптации человека с диабетом в обществе. Крайне важно изменить поведение больного и научить его грамотно управлять своим состоянием за счет активного вовлечения в лечебный процесс, который невозможен без мониторинга гликемии.
Таким образом, становится очевидной необходимость внедрения новых подходов к оценке контроля углеводного обмена при СД.
В феврале 2017 г. на Конгрессе ATTD (Advanced Technologies and Treatment for Diabetes) группой экспертов принят Международный консенсус по использованию непрерывного мониторинга гликемии (НМГ). Ниже приведены наиболее важные положения консенсуса, которые распространились и на данные, получаемые при самоконтроле гликемии с помощью глюкометра с мобильным приложением.
1. Поскольку высокая вариабельность гликемии служит предиктором развития гипогликемии и сопровождается повышенным риском летального исхода, рекомендуется оценивать стандартное отклонение, коэффициент вариации (КВ) и среднюю амплитуду колебаний глюкозы в качестве показателей вариабельности гликемии. КВ является предпочтительным способом и рассчитывается как отношение стандартного отклонения к среднему значению величины, измеряемое в процентах. Гликемия считается стабильной при КВ менее 36% и нестабильной – при КВ более 36%.
2. Рекомендовано использовать параметр «time in range» – время нахождения в диапазоне целевых значений гликемии (3,9–10,0, реже 3,9–7,8 ммоль/л), дающий более развернутую информацию о текущем состоянии гликемического контроля по сравнению с HbA1c.
3. Следует рассчитывать в процентах периоды пребывания в следующих диапазонах: 2-й уровень гипогликемии (менее 3,0 ммоль/л), 1-й уровень гипогликемии (3,9–3,0 ммоль/л), целевые значения (3,9–10,0 или 3,9–7,8 ммоль/л); 1-й уровень гипергликемии (10,0–13,9 ммоль/л), 2-й уровень гипергликемии (более 13,9 ммоль/л). Этот метод очень удобен для оценки эффективности лечения, а также помогает пациентам увидеть, как изменяются частота и выраженность гипо- и гипергликемии на фоне лечения.
4. Стоит также выделять блоки времени: период сна (00,00–06,00), пробуждения (06,00–12,00), весь день (00,00–24,00), что позволяет более прицельно проводить коррекцию терапии [11].
В настоящее время подобные отчеты формируются в мобильных приложениях глюкометров-систем.
Поэтому сохраняется актуальность более широкого использования современных средств мониторинга гликемии с мобильными приложениями при проведении самоконтроля и обучения пациентов работе с ними.
Появление глюкометров, передающих данные на мобильное приложение для смартфона или айфона, предоставило реальную возможность улучшения показателей гликемического контроля у больных СД, позволяя пациентам и врачам обмениваться информацией дистанционно (при помощи текстовых сообщений или электронной почты). Это может приводить к минимизации частоты обращений в амбулаторные медицинские учреждения [12]. Показано, что мобильные медицинские технологии (mHealth) позволяют улучшать показатели HbA1c, а также эффективны для установления дистанционного обмена информацией между пациентами и врачами [13].
По представленным данным опроса в Интернете наиболее часто применяемой технологией является обмен текстовыми сообщениями (смс). Использование данной опции в мобильных медицинских технология (mHealth) также может способствовать большему вовлечению определенных категорий пациентов в управление диабетом [14].
В настоящее время мобильные технологии получили широкое распространение. Имеются данные о возможности их использования для достижения индивидуальных целей гликемического контроля у пациентов как с СД1, так и СД2. По результатам мета-анализа, технологии, основанные на использовании мобильных телефонов, позволили снижать уровень HbA1c на 0,5% за 6 месяцев с более выраженным снижением уровня HbA1c у больных СД2 (0,8%) по сравнению с пациентами с СД1 (0,3%) [15]. Кроме того, в обзоре результатов 13 исследований установлена статистически значимая позитивная динамика показателей гликемического контроля у пациентов СД2, использующих для обмена данными короткие сообщения, по сравнению c очными визитами к врачу [16].
Обмен текстовыми сообщениями (смс) между пациентами и лечащим врачом может влиять на клинические исходы больных. Это продемонстрировано в исследовании по оценке влияния обмена смс на гликемический контроль у пациентов с СД2 в Саудовской Аравии. Было показано, что использование 5–7 текстовых сообщений в неделю коррелировало со снижением HbA1c через 4 месяца [17]. В работе по оценке эффективности ежедневных текстовых сообщений (смс) от медсестры по сравнению с еженедельными телефонными контактами выявлено сопоставимое снижение уровня HbA1c в каждой группе. Таким образом, использование смс может расцениваться как дополнительный метод улучшения контроля СД [18].
Глюкометры-системы
Новые достижения в области облачного программного обеспечения и мобильных приложений по контролю СД, которые используются совместно с глюкометрами, позволили разработать новые модели взаимодействия между пациентами и врачами [19]. Современные глюкометры-системы дают возможность людям с СД самостоятельно оценивать важнейшие параметры обмена веществ с точностью, близкой к лабораторной в привычной для пациента обстановке. Именно самоконтроль гликемии является наиболее важной опцией для подбора терапии, чем исследования гликемии, выполняемые в условиях поликлиники или стационара.
Одним из таких современных глюкометров-систем является Contour Plus One (Контур Плюс Уан) с мобильным приложением – Contour Diabetes (Контур Диабитис). Глюкометр-система оснащена множеством полезных функций, особенно важных для пациентов на интенсифицированной инсулинотерапии.
Глюкометр-система Контур Плюс Уан предназначена для самостоятельного проведения исследования уровня глюкозы пациентами с СД или врачом/медицинской сестрой. Прибор не требует кодирования, т.к. это происходит автоматически. Оценка уровня глюкозы осуществляется в венозной крови, свежей цельной капиллярной крови, полученной из подушечки пальца. Глюкометр-система предназначена для измерения уровня глюкозы в цельной крови в диапазоне от 0,6 до 33,3 ммоль/л и работает с тест-полосками Contour Plus (Контур Плюс), обеспечивая точность измерений при температуре от 5 до 45°C. Важно помнить, что система Контур Плюс Уан не предназначена для подтверждения диагноза диабета или для его выявления в ходе скрининга. Система также не подходит для контроля гликемии у новорожденных.
Аналитическая точность устройства полностью соответствует требованиям стандарта ISO 15197:2013. Согласно результатам лабораторного исследования, 100% получаемых результатов находятся в пределах установленных диапазонов значений гликемии (±15% и ±0,83 ммоль/л для уровней глюкозы в крови ≥5,6 и <5,6 ммоль/л соответственно) и в зоне A согласительной решетки ошибок Паркса [20]. Оценка точности измерения при использовании технологии «Второй шанс» продемонстрирована в клиническом исследовании, где приняли участие 52 пациента с СД. Каждый испытуемый 2 раза измерял уровень глюкозы в крови с помощью прибора. Предпринято 104 попытки нанесения образца крови на тест-полоски из двух партий, 85 результатов были включены в анализ (время, прошедшее между первым и вторым нанесениями, составляло 6–52 секунды). Критерии точности исследования соответствовали разделу 8.2 стандарта ISO 15197:2013. Результаты, полученные после повторного нанесения, сравнивали со средним значением результатов измерений, проведенных на анализаторе YSI 2300 Stat Plus (YSI Life Sciences, Inc., Yellow Springs, OH, USA) до и после повторного нанесения.
Точность измерений сохранялась при повторном нанесении образца крови. При использовании технологии «Второй шанс» 100% (85 из 85 результатов) измерений находились в диапазоне ±15% или ±0,83 ммоль/л от результатов сравнительного лабораторного метода при концентрациях ≥5,55 и <5,55 ммоль/л соответственно [21].
В глюкометре-системе важно использовать такие функции, как:
- дата и время, которые необходимо установить во время первоначальной настройки прибора, что поможет в дальнейшем анализировать и правильно оценивать результаты измерения глюкозы крови;
- целевой диапазон гликемии для интерпретации результата (рис. 2);
- метки «До еды» и «После еды», которые рекомендуется добавлять к результатам измерения.
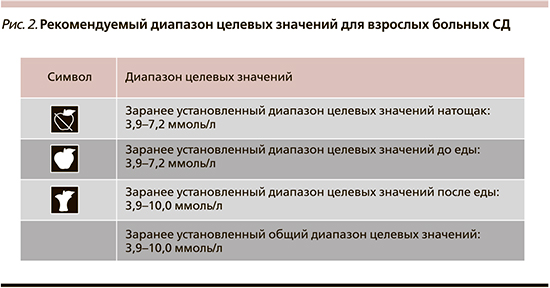
Контроль ГПН помогает оптимизировать дозу базального инсулина, показатели гликемии «До еды» и «После еды» – дозу болюсного инсулина. Отметки о еде подскажут, как различные виды пищи и размеры порций влияют на уровень глюкозы крови:
- добавление фотографии употребляемой пищи, что позволяет точнее учитывать содержание углеводов в пище,
- голосовые заметки, которые дают дополнительное объяснение ситуации, например динамику гликемии при физических нагрузках;
- средние значения гликемии вместе с показателями ГПН. Это поможет оптимизировать дозу базального инсулина. Если средние значения гликемии за последние 7 дней наблюдения меньше, чем за 30 дней, то это свидетельствует об улучшении контроля гликемии;
- тренды гликемии: эта функция позволяет быстрее и точнее анализировать показатели и выявлять тенденции изменений гликемии по сравнению с обычным дневником самоконтроля. При выявлении повторяющихся эпизодов гипо- (не менее 2 эпизодов за 3-часовой интервал) или гипергликемии (не менее 3 эпизодов за 3-часовой интервал) на протяжении 5 дней глюкометр-система автоматически выводит информацию с предупреждением на экран. Это позволяет сокращать время анализа записей в дневниках диабета, число неправильных интерпретаций результатов, а также снижать риск развития тяжелых гипогликемических состояний;
- звуковые и визуальные сигналы при гипо- и гипергликемии. Эти полезные функции глюкометра уменьшают вероятность ошибок при самостоятельном тестировании. Благодаря сигналам глюкометра пациенты могут быстро принимать необходимые меры и обращаться за помощью в случае ухудшения состояния до того, как ситуация станет критической;
- цветная подсветка порта (smartLIGHT) для введения тест-полосок позволяет мгновенно сообщать, в каком диапазоне находится гликемия по сравнению с диапазоном целевых значений до еды, после еды или общим диапазоном целевых значений: в целевом диапазоне (зеленый цвет), выше целевого (желтый цвет), ниже цели (красный цвет). Если результат определения уровня глюкозы в крови ниже целевого значения, глюкометр-система дополнительно дважды издает звуковой сигнал. Достаточно мощная подсветка позволяет проводить тестирование в условиях недостаточного освещения (рис. 3).
- технология «Второй шанс» (Second-Chance®) позволяет добавлять на тест-полоску кровь из той же капли, если первого образца оказалось недостаточно, не делая еще одного прокола. Это никак не отражается на точности измерений. После нанесения тестируемого образца на тест-полоску, для чего надо лишь коснуться ее заборным концом капли крови, которая втянется сама за счет силы капиллярного всасывания, прибор оценит, достаточен ли объем для корректного тестирования. Если нет – прибор дважды издаст звуковой сигнал, а на экране появится изображение недозаполненной тест-полоски и на дополнительное нанесение крови у пациента имеется 60 секунд. Объем образца крови, необходимый для проведения тестирования, составляет всего 0,6 мкл (рис. 4).

В приложении Контур Диабитис предусмотрена возможность напоминаний о проведении тестирования через разные промежутки времени времени от начала приема пищи (от 30 минут до 2 часов с шагом 30 минут) или использования одного из предложенных 11 планов напоминаний об измерениях. В памяти глюкометра может храниться 800 результатов измерений, а в приложении и облачном хранилище – неограниченное количество показаний.
Приложение дает возможность вести дневник диабета в электронном виде, к показателям глюкозы крови, которые передаются из глюкометра по Bluetooth, можно добавлять информацию о питании, ХЕ, физической активности, получаемой терапии, формировать графики с данными для быстрой оценки.
«Облачное» приложение позволяет врачам наблюдать за течением заболевания у пациентов, обеспечивает возможность дистанционного консультирования, суммирует результаты измерения гликемии и формирует аналитические отчеты.
В настоящее время многие пациенты не фиксируют результаты самоконтроля на бумажных носителях. Интенсивное дистанционное взаимодействие между врачом и пациентом позволяет осуществлять мониторинг показателей гликемии и оперативно проводить лечение, оценивать его эффективность, корректировать поведение пациентов. Сам факт того, что пациент знает о доступности показателей его гликемии для врача, является мощным стимулом для соблюдения рекомендаций, изменения образа жизни, повышения мотивации на достижение цели лечения.
Таким образом, мобильное приложение Контур Диабитис – это электронный дневник самоконтроля, который автоматически собирает и сохраняет результаты, показывает данные в удобном формате (диаграммы, графики, тренды, цветовые подсказки), позволяет формировать и делиться отчетами (e-mail, СМС и др.), быстро выявлять потенциальные проблемы, способствует вовлечению пациента в управление диабетом, экономит время на приеме врача.
Заключение
Современные глюкометры-системы с мобильным приложением позволяют более оперативно управлять гликемией, повышать приверженность пациентов активному управлению заболеванием, достигать цели лечения с использованием инновационных технологий.
Вклад авторов. М.Б. Анциферов – разработка дизайна статьи, утверждение рукописи для публикации. О.М. Котешкова – обзор публикаций по теме статьи, написание текста рукописи.



