Введение
Бaктериальный вагиноз (БВ) – дисбиоз, характеризующийся снижением числа лактобактерий, инверсией их структуры в пользу Lactobacillus iners и увеличением количества условно-патогенных анаэробных микроорганизмов, таких как Gardnerella vaginalis, Atopobium vaginae, Prevotella spp., БВ-ассоциированных бактерий [1].
В нaстоящее время БВ рассматривается как глобaльная проблема с высокой распространенностью среди населения (23–29% женщин репродуктивного возраста в общей популяции во всем мире) и высокими экономическими затратами на его лечение (4,8 млрд долл. в год в США) [2]. БВ повышает риск заражения и передачи ВИЧ/ИППП (инфекции, передаваемые половым путем), гинекологических заболеваний и неблaгоприятных исходов беременности, включая сaмопроизвольные выкидыши, преждевременные роды, низкую массу ребенка при рождении и послеродовый эндометрит [3–4].
Этиология БВ до сих пор является предметом дискуссий среди исследователей. C.A. Muzny et al. считают, что наличие G. vaginalis может быть необходимым, но недостаточным для развития БВ и заболевание возникает в результате инфицирования вирулентными штаммами G. vaginalis и Prevotella bivia (первичные колонизаторы), к которым впоследствии присоединяются A. vaginae и другие БВ-ассоциированные бактерии (вторичные колонизаторы) [5]. Продукты их метаболизма запускают высвобождение провоспалительных цитокинов, что приводит к деградации слизи, повреждению эпителиального барьера, воспалительной реакции слизистых оболочек влагалища, что позволило авторам сформулировать новую парадигму патогенеза БВ. При этом иммунологические сдвиги способствуют снижению эффективности лечения и повышению риска рецидивов БВ [5]. Концентрация доминирующих видов бактерий у 64% женщин через 12 недель после лечения БВ антибактериальными средствами возвращается к исходному уровню, а концентрация цитокинов при персистирующем БВ сохраняется на высоком уровне [5], и эти показатели рассматриваются как предикторы рецидивов [6].
Свой вклад в развитие рецидивов БВ вносят сочетанные инфекции, распространенность которых составляет от 4,4 до 36% [7, 8]. Риск БВ и его рецидивов увеличивается в присутствии вирусов герпеса (ВГ) с отношением шансов (ОШ) 1,55 (95% доверительный интервал [ДИ]: 1,30–1,84) [9] и предстaвляет серьезную проблему, поскольку инфицированность вирусами простого герпеса (ВПГ) 1-го и 2-го типов в мире составляет 80% [10]. Особенности развития (течения) инфекционного процесса при сочетанных инфекциях обусловлены компонентным составом микробных ассоциаций, обусловливающим эффект синергизма в формирующемся биоценозе, и видом доминирующей инфекции, при этом наблюдается повышенная устойчивость к противомикробным препаратам и более длительное время, необходимое для выздоровления хозяина [11].
Таким образом, важно определять все разнообразие микроорганизмов и вирусов, состояние иммунной защиты влагалища при РБВ у пациенток, инфицированных ВПГ, для полного понимания этиологии заболевания и поиска оптимальных методов лечения.
Цель исследования: изучить особенности микробиоценоза влагалища и локального иммунитета у пациенток с рецидивирующим БВ, инфицированных ВПГ.
Методы
Исследование выполнено на базе женских консультаций Махачкалы с января 2020 по январь 2021 г. Были включены 100 пациенток после подписания информированного добровольного согласия на участие в исследовании. Они были разделены на 2 группы: I (n=80) – с установленным клиническим диагнозом РБВ и ВПГ и II (n=20) – условно здоровые (для контроля лабораторных показателей).
Критерии включения в исследование: возраст от 18 до 45 лет; диагноз В96.8 – Другие уточненные бактериальные агенты как причина болезней, классифицированные в других рубриках (повторный эпизод клинических проявлений БВ) в сочетании с А60.0 – Герпетические инфекции половых органов и мочеполового тракта (N77.1); письменное информированное добровольное согласие пациентки.
Критерии исключения: беременность и кормление грудью, наличие ИППП (кроме вирусных), аномальное маточное кровотечение, использование гормональных контрацептивов или антибиотиков, сорбентов, пре- и пробиотиков менее чем за 3 месяца до включения в исследование, лекарственных средств или контрацептивов, применяемых вагинально (кроме мужских презервативов), наличие тяжелой соматической патологии, заболеваний эндокринной системы (сахарный диабет, гипотиреоз), печеночной или почечной недостаточности, психических нарушений; участие в ином клиническом исследовании за 30 дней до включения в настоящее исследование.
Методы исследования включали оценку жалоб и анамнеза, гинекологическое обследование, рН-метрию содержимого влагалища и аминный тест, простую микроскопию влагалищных мазков, окрашенных по Грамму; определение бактерий в отделяемом влагалища методом «Фемофлор-16» (ООО «ДНК-Технология», Россия), ИППП (хламидии, гонококки, трихомонады, микоплазмы), вирусов папилломы человека (ВПЧ), герпесвирусов 1-го, 2, 4, 5-го типов методом полимеразной цепной реакции («Проба НК»); содержание интерлейкина-1β (ИЛ-1β), -2, -6, -8, интерферона-γ (ИФН-γ), фактора некроза опухоли-α (ФНО-α), ИЛ-4, -10 во влагалищном секрете методом иммуноферментного анализа (сендвич-ELISA, наборы фирмы «Цитокин», Санкт-Петербург).
Исследование выполнялось в соответствии с Правилами клинической практики (GCP) в Российской Федерации (Приказ Минздрава РФ № 26 6от 19.06.2003).
Статистическая обработка данных проводилась с применением интегральной системы для комплексного статистического анализа и обработки данных «Statistica 6» и «Microsoft Excel 2000». Определяли нормальность распределения показателей (критерий Колмогорова–Смирнова), представляли количественные данные в виде средней величины и стандартного отклонения M (SD), качественные – в абсолютных числах (n) и относительных величинах (%). Статистическую значимость различий средних величин оценивали в независимых выборках с помощью U-критерия Манна–Уитни. Критический уровень значимости принимался при р<0,05. Для проверки гипотезы значимости различий между группами использовался χ2-критерий для четырехпольной таблицы. Для демонстрации силы связи вычисляли 95% ДИ для ОШ по методу Woolf. Если ДИ для ОШ включал 1,0, то анализируемый признак не имел значимости. Если все значения ДИ были выше 1,0, изучаемый признак являлся значимым.
Результаты
Анализ полученных данных показал, что средний возраст пациенток, включенных в исследование, составил 31,8 (5,3) года. В возрастной структуре обследованных преобладали пациентки 26–35 лет (65% [52/80] и 70% [14/20]; р=0,87) в соответствующих группах. Общие сведения о пациентках представлены в табл. 1.

Группы имели статистически значимую разницу только по одному показателю – заболеваниям мочевыделительной системы (ОШ=4,88, 95% ДИ: 1,32–17,96; р=0,02).
Частота выявления условно-патогенных микроорганизмов (УПМ) представлена в табл. 2.
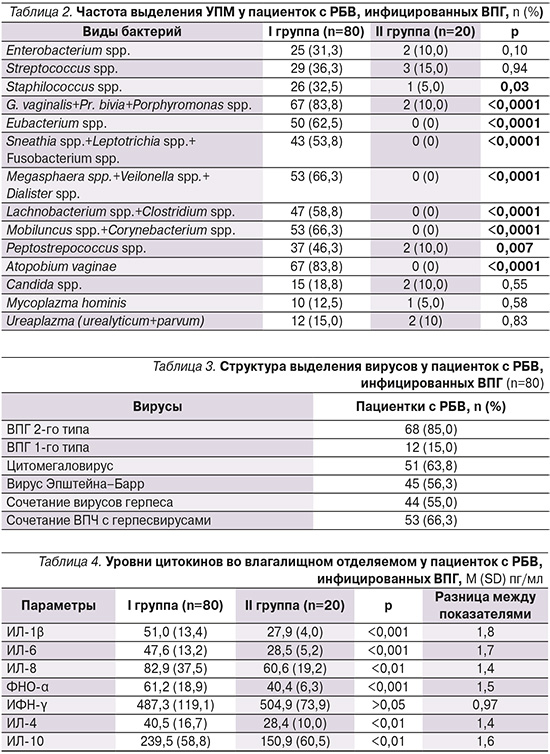
Наиболее часто у пациенток выявлялись G. vaginalis+Pr. bivia+Porphyromonas и A. vaginae – у 83,8% (67/80) пациенток. Относительный шанс их выявления у пациенток с БВ и ВПГ по сравнению со здоровыми составлял 46,38 (95% ДИ: 9,58–224,53; р<0,0001). На втором месте по частоте были бактерии рода Megasphaera spp. и Mobiluncus spp. − у 66,3% (53/80) пациенток (ОШ=37,3, 95% ДИ: 4,74–293,69; р<0,0001). Другие БВ-ассоциированные бактерии встречались с частотой от 46,3 до 62,5%. В дополнение к этому статистически значимо чаще обнаруживались Staphilococcus spp. – у 32,5% (26/80, ОШ=9,15, 95% ДИ: 1,6–72,11; р=0,03). Сочетание с Candida spp. не было статистически значимым.
Наиболее часто встречаемым ВПГ у пациенток с БВ был ВПГ 2-го типа – 85% (68/80), у 66,3% (53/80) выявлено сочетание с ВПЧ и у 55% (44/80) – сочетание различных типов вирусов герпеса (табл. 3).
Данные о содержании цитокинов во влагалищном отделяемом у обследованных пациенток представлены в табл. 4. Выявлены статистически значимо более высокие показатели цитокинов у пациенток с РБВ, инфицированных ВПГ, по сравнению с женщинами с нормальным микробиоценозом влагалища: ИЛ-1β – в 1,8 раза; -6 – в 1,7; ФНО-α – в 1,5 раза (р<0,001) и ИЛ-8 – в 1,4; -4 – в 1,4; -10 – в 1,6 раза (р<0,01).
Содержание ИФН-γ между группами не имело статистически значимой разницы.
Таким образом, у пациенток с РБВ, инфицированных ВПГ, кроме G. vaginalis, Pr. bivia и A. vaginae отмечается высокая частота выявления Megasphaera spp., Mobiluncus spp. (66,3%) и Staphilococcus spp. (32,5%), кроме ВПГ выявлено сочетание с ВПЧ (66,3%) и другими типами вирусов герпеса (55%), что сопровождается повышением уровней цитокинов, преимущественно провоспалительных: ИЛ-1β – в 1,8 раза; -6 – в 1,7; ФНО-α – в 1,5 раза (р<0,001), и противовоспалительного ИЛ-10 – в 1,6 раза (р<0,01).
Обсуждение
В современной литературе изучению этиологии БВ уделяется большое внимание, и благодаря методу полногеномного секвенирования были открыты важные свойства основного возбудителя БВ – G. vaginalis, такие как существование 13 видов и их различный уровень патогенности, среди которых наибольшей обладают G. vaginalis (подгруппа C) и G. Piotii (подгруппа B) [5]. Наряду с G. vaginalis раскрыта роль P. bivia как первичного колонизатора, который усиливает вирулентные свойства гарднерелл, способствуя их адгезии к клеткам эпителия влагалища и изменяя белки и метаболиты, связанные с физико-химическим барьером (муцины, сиаловая кислота, полиамины) [5]. Показано, что присутствие A. vaginae в образцах бактериальной биопленки, полученных от пациентов с БВ, вызвано G. vaginalis и варьируется, по данным разных авторов, от 54 до 96% [12]. A. vaginae и S. amnii вызывают сильные провоспалительные и проонкогенные реакции посредством индукции цитокинов, iNOS и окислительного стресса, полимикробная инфекция приводит к наиболее выраженной иммунной и метаболической активности, а L. iners модулируют метаболом внеклеточного цервико-влагалищного микроокружения [13, 14].
Известно, что инфекция, вызванная ВПГ-2, увеличивает риск БВ, но обратное влияние не изучалось. Ch. Johnston et al. обратили внимание на то, что выделение ВПГ-2 приводит к увеличению присутствия и числа БВ-ассоциированных бактерий и усиливает воспаление [15], а L. Masese et al. на основании своего исследования утверждают, что заражение ВПГ-2 увеличивает риск последующих эпизодов БВ на 28% и что существует причинно-следственная связь между инфекцией ВПГ-2 и нарушением вагинальной микробиоты [16]. В исследовании K.A. Stoner et al. эффективность терапии БВ метронидазолом была намного ниже, чем сообщалось ранее в исследованиях, не ограничивающих участия женщин с серопозитивностью к ВПГ-2, кроме того, авторы наблюдали частоту рецидивов БВ 89% в первый месяц после завершения терапии [17].
Обследование пациенток с рецидивирующим течением БВ и выделением ВПГ показало разнообразие вагинального микробиома и кроме G. vaginalis, P. bivia и A. vaginae у большинства пациенток выделялись Megasphaera spp., Mobiluncus spp. (66,3%) и Staphilococcus spp. (32,5%), более чем у 50% пациенток выделены также и другие БВ-ассоциированные бактерии (Eubacterium spp., Sneathia spp., Leptotrichia spp., Fusobacterium spp., Lachnobacterium spp., Clostridium spp.). Такое разнообразие имеет клиническое значение, поскольку исследование чувствительности бактерий, ассоциированных с БВ, показало, что они обладают разной устойчивостью к рекомендуемым средствам лечения: к метронидазолу устойчивы A. vaginae, Mobiluncus spp., а к клиндамицину – P. bivia, S. amnii, Prevotella spp. со значениями МИК90 >128 мкг/мл [18], что приводит к их неполной элиминации при лечении одним из антибиотиков и создает условия для персистенции, возврату к исходному уровню доминирующих видов бактерий и развитию рецидивов [5]. Иммунометаболические профили микросред, связанных с наиболее распространенными четырьмя видами бактерий при БВ, показали, что A. vaginae и S. amnii продемонстрировали самый высокий провоспалительный потенциал за счет индукции цитокинов, iNOS и соединений, вызванных окислительным стрессом, G. vaginalis и P. bivia отчетливо изменяют физико-химические белки и метаболиты, связанные с эпителиальным барьером (муцины, сиаловая кислота, полиамины) [14].
Некоторые исследователи показали, что Staphilococcus spp. также связаны с БВ [19, 20], однако частота их обнаружения у пациенток с БВ была ниже, чем в настоящем исследовании, что может быть, возможно, объяснено присутствием вирусов и измененной иммунной защитой, что подтверждается одним из исследований, где было показано, что ИЛ-1β, -8 и -6 в концентрациях, аналогичных таковым во влагалище здоровых женщин, стимулируют рост нормальной микрофлоры (Lactobacillus spp.) и подавляют рост и образование биопленок Staphilococcus aureus и Escherichia coli. Напротив, эти цитокины в более высоких концентрациях, характерных для дисбактериоза влагалища, подавляли нормальную микрофлору и стимулировали рост УПМ, а ФНО при обоих состояниях оказывал стимулирующее действие на исследуемые вагинальные микросимбионты [21]. Косвенным подтверждением этого положения может быть наличие у обследованных нами пациенток с РБВ более высокой частоты заболеваний мочевыделительный системы по сравнению со здоровыми (ОШ=4,88, 95% ДИ: 1,32–17,96; р=0,02).
Кроме того, нами выявлено, что у большинства пациенток имеет место сочетание БВ/ВПГ с ВПЧ (66,3%) и другими типами вирусов герпеса – цитомегаловирусом и вирусом Эпштейна–Барр (55%). Степень связи между БВ и ВПЧ варьируется в эпидемиологических исследованиях и остается противоречивой. Тем не менее мета-анализ 6 исследований показал ОШ=2,68, 95% ДИ: 1,64–4,40; p<0,001, что указывает на положительную связь между БВ и ВПЧ-инфекцией [22].
G. vaginalis и Prevotella spp. значительно чаще определялись у пациенток с ВПЧ [23]. Выдвинуто несколько гипотез, подтверждающих эту связь: с одной стороны, БВ связан со снижением уровня ингибитора секреторной лейкоцитарной протеазы (SLPI), способного блокировать вирусную инфекцию in vitro, с другой – ферменты, выделяемые при БВ, разрушают защитный барьер слизистой оболочки, следовательно, повышают восприимчивость к ВПЧ [22]. Также имеются указания, что иммунологический баланс в ткани шейки матки меняется в результате выработки цитокинов [24]. Более позднее исследование подтверждает, что распространенность БВ выше в 2 раза у пациенток с ВПЧ высокого канцерогенного риска [25]. Однако P. Romero-Morelos et al., изучавшие распространенность A. vaginae и G. vaginalis у пациенток с ВПЧ, не смогли подтвердить ассоциацию указанных микроорганизмов с ВПЧ [26].
Большинство исследователей сходятся во мнении, что у пациенток с высоким разнообразием микробиоты влагалища, характерным для БВ, число цервикальных CD4+ Т-клеток связано с инфекцией ВПГ-2 и отчетливым провоспалительным цитокиновым профилем [27], что совпадает с результатами настоящего исследования.
По данным литературы, колонизация влагалища пациенток с БВ грибами составляет 33,1% и сообщества с преобладанием L. iners с большей вероятностью содержат Candida (в 3 раза выше), чем сообщества с преобладанием L. crispatus с ОШ=2,9, 95% ДИ: 1,03–7,21; p=0,048 [28, 29]. Однако в настоящем исследовании такой зависимости выявлено не было: сочетание с Candida spp. (18,8%) не было статистически значимым, что совпадает с исследованием женщин, инфицированных ВПГ, где частота выделения Candida spp. тоже была ниже (20%) [30]. Т.Н. Бебнева и соавт. обнаружили отрицательную корреляцию в отношении всех типов ВПЧ с Candida spp. [31].
Присутствие G. vaginalis, A. vaginae, Megasphaera spp. и Mobiluncus spp. характеризуется уровнями ИЛ-1β, -4, ИЛ-6, -8, -10 и ФНО-α в среднем в 1,6 раза выше, чем при нормоценозе. Эти данные подтверждаются результатами других исследований, свидетельствующих о сдвигах цитокинового статуса БВ-положительных женщин в пользу повышения уровня провоспaлительных цитокинов, чем БВ-негативных [32, 33]. В отношении противовоспалительных цитокинов мнения разошлись, и О. Hruzevskyi отметил снижение уровней ИЛ-4 и -10 у пациенток с персистирующим дисбиозом [34]. Присутствие в организме ВПГ-2 также запускает высвобождение ФНО-α [35], способствует увеличению содержания G. vaginalis [36]. Все эти изменения снижают эффективность лечения и повышают риск рецидивов БВ [37].
Заключение
На основании выполненного исследования можно сделать следующие выводы: у пациенток с РБВ, инфицировaнных ВПГ, наблюдается видовое рaзнообразие микрофлоры влагалища, включающее кроме анаэробных бактерий Staphilococcus spp. сочетание вирусов герпеса и ВПЧ. Реакция локальной иммунной системы на инфекционные антигены характеризуется повышением уровней про- и противовоспалительных цитокинов в среднем в 1,6 раза. Это обосновывает необходимость комплексного лечения с использованием не только антимикробных препаратов, но и средств иммуномодулирующего действия.
Вклад авторов. Г.Б. Дикке, З.А. Абу-суева – концепция и дизайн исследования. Б.М. Айсаева – сбор и обработка материала. Б.М. Айсаева, Г.Б. Дикке – написание текста и его редактирование после рецензирования. П.Ж. Гитинова – статистическая обработка данных.
Дополнительная информация
Публикация статьи осуществляется в рамках диссертационной работы: «Иммуноопосредованные механизмы рецидивирующего бактериального вагиноза у женщин, инфицированных вирусом простого герпеса».



