Введение
Новая коронавирусная инфекция (SARS-CoV-2, COVID-19), изначально начавшаяся в Китае (провинция Ухань) в конце 2019 г. как эпидемия [1], на данный момент распространилась на весь мир и официально была признана Всемирной организацией здравоохранения (ВОЗ) пандемией из-за высоких темпов роста заболеваемости и смертности [2, 3].
Быстрые темпы распространения COVID-19, обусловленные в т.ч. воздушно-капельным, воздушно-пылевым и контактными путями передачи инфекции, приводт к значительному увеличению объема профессиональной нагрузки, возлагаемой на первичное звено здравоохранения [4].
На данный момент в мире не существует единого этиологического лечения, направленного против новой коронавирусной инфекции. Однако ведущими медицинскими сообществами мира регулярно разрабатываются и обновляются методические и клинические рекомендации по ведению данной патологии. Кроме того, согласно рекомендациям ВОЗ, возможно назначение препаратов с предполагаемой этиотропной эффективностью «off-label» [1].
В связи с этим крайне необходимо, чтобы первичное звено здравоохранения было достаточно осведомлено о современных подходах к лечению коронавирусной инфекции и непосредственно использовало их на практике в борьбе с пандемией.
Цель исследования: оценить предпочтения специалистов амбулаторного звена г. Белгорода в выборе схем лечения новой коронавирусной инфекции и их соответствие официальным рекомендациям.
Методы
В рамках текущего исследования проанализировано 156 клинических случаев (случайная выборка из амбулаторных карт) терапии пациентов с предполагаемой или подтвержденной новой коронавирусной инфекцией в Городской поликлинике Белгорода (поликлиническое отделение № 2), относящихся к периоду с марта по декабрь 2020 г. Все пациенты были включены в COVID-реестр лечебно-профилактического учреждения (ЛПУ), на базе которого проводилось исследование. Часть из них имели несколько случаев обращения в первичное звено и получали лечение по разным нозологическим единицам (ОРВИ, внебольничная пневмония, COVID-19). В период проведения исследования авторами также проводились образовательно-информационные мероприятия в ЛПУ, внедрение алгоритмов, направленных на повышение качества терапии, в т.ч. в отношении рационального применения антимикробных препаратов [11].
Для сравнительного анализа все клинические случаи были разделены на две группы: пациенты, получавшие терапию до подтверждения COVID19, либо с отрицательным ПЦР-тестом (в дальнейшем – группа COVID-19 [-]), и пациенты, получавшие терапию после лабораторной идентификации COVID-19 (в дальнейшем группа COVID-19 [+]).
Фиксировали как «случаи назначения» той или иной группы препаратов в целом (% от количества эпизодов лечения), так и общее «количество назначений» (k) лекарственных средств (ЛС) на эпизод лечения, когда пациенту было одновременно или последовательно назначено несколько ЛС одной группы. Были учтены и проанализированы следующие группы ЛС: «Противовирусные ЛС», «Иммуномодулирующие ЛС», «Антибактериальные ЛС», «Антикоагулянты и антиагреганты», «Муколитики и противокашлевые ЛС», «Витамины», «Глюкокортикостероиды», «Прочие ЛС». Сравнивались абсолютные, относительные показатели, статистическая значимость оценена с помощью критериев «р» и «z». Данные вносились и обрабатывались в приложении Microsoft Excel.
Результаты
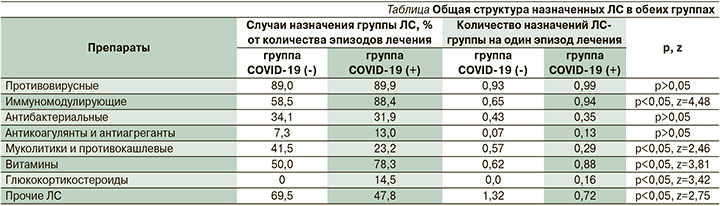
В группе COVID-19 (-) проанализировано 82 посещения, из них женщины составили 53 (64,6%) случая. В группе COVID-19 (+) проанализировано 69 случаев, женщин – 44 (63,8%). В группе COVID-19 (-) наиболее часто назначались противовирусные средства. Они были назначены в 89% случаев, при этом количество назначений ЛС этой группе составило 0,93 на один эпизод лечения. В группу «Прочие ЛС» вошли следующие лекарственные средства: диоксометилтетрагидропиримидин (Метилурацил), группа антигистаминных препаратов, пробиотиков и α-адреномиметиков, нитрофурал (Фурацилин), грамицидин С+цитилпиридиния хлорид (Граммидин), морская вода (Аква Марис), парацетамол, бензидамин (Тантум Верде), бензилдиметил (Мирамистин), кальция добезилат (Докси-Хем). Данные препараты назначены в 69,5% случаев (k=1,32). Реже назначались иммуномодулирующие средства (58,5%, k=0,65), витамины (50%, k=0,62), муколитики и противокашлевые препараты (41,5%, k=0,57), а также антибактериальные препараты (34,1%, k=0,43). На долю антикоагулянтов и антиагрегантов приходилось 7,3% назначений (k=0,073).
В группе COVID-19 (+) значительно чаще (статистически значимо) имело место назначение иммуномодулирующих средств (88,4%, k=0,94; p<0,05, z=4,48) и витаминов (78,3%, k=0,88; p<0,05, z=3,81). Противовирусные средства назначались так же часто, как и в группе COVID-19 (-) (89,9%, k=0,99; p>0,05), роль средств группы «Прочие ЛС» снизилась до 47,8% (k=0,72; p<0,05, z=2,75), а группы муколитиков и противокашлевых препаратов до 23,2% (k=0,29; p<0,05, z=2,46), антибактериальные средства назначались в 31,9% случаев (k=0,35; p>0,05), в этой группе также назначались глюкокортикостероиды (14,5%, k=0,16; p<0,05, z=3,42), а также антикоагулянты и антиагреганты в 13% случаев (k=0,13; p>0,05). Общая структура назначенных ЛС в обеих группах приведена в таблице.
Согласно рекомендациям, лечение COVID-19 должно проводиться среди как подтвержденных случаев, так и вероятных случаев инфицирования. В качестве этиотропного лечения COVID-19 на данный момент рекомендуется применять следующие препараты: фавипиравир, молнупиравил, ремдесивир, синтетическую малую интерферирующую рибонуклеиновую кислоту (двуцепочечную)], умифеновир и интерферон-α [1, 5].
В нашем исследовании среди противовирусных средств самым назначаемым препаратом в группе COVID-19 (-) был рекомендованный к применению умифеновир (Арбидол) – 71,1%, также применялись Кагоцел – 2,6%, имидазолилэтанамид пентандиовой кислоты (Ингавирин) – 9,2%, энисамия йодид (Нобазит) – 17,1%.
Умифеновир занимает лидирующее положение и в группе COVID-19 (+): он назначался в 79,4% случаев; также в назначениях появляется фавипиравир с частотой назначения 10,3%. Другие не рекомендованные к применению препараты при подтвержденной коронавирусной инфекции распределились следующим образом: имидазолилэтанамид пентандиовой кислоты – 5,9% назначений, энисамия йодид – 2,9%, риамиловир (Триазавирин) – 1,5%.
Среди группы иммуномодулирующих средств единственным рекомендованным к применению является интерферон-α [1]. В обеих группах он имеет самый высокий средний показатель назначения среди иммуномодулирующих препаратов (79,2% в COVID19 [-] и 89,2% в COVID-19 [+]). Остальные препараты в обеих группах не имели значимой доли. В группе COVID-19 (-) применялись такие ЛС: интерферон-γ (Ингарон), азоксимера бромид (Полиоксидоний), дезоксирибонуклеат натрия (Деринат) – все с частотой 1,9%; лизаты бактерий (Бронхомунал) – 3,8, меглюмина акридонацетат (Циклоферон) – 11,3%. В группе COVID-19 (+): меглюмина акридонацетат – 6,2, лизаты бактерий – 4,6%.
COVID-19 – это вирусная инфекция, в большинстве случаев не требующая для лечения применения антибактериальных средств (АБС). Антибиотики применяются только при наличии убедительных признаков присоединения бактериальной инфекции (повышение уровня прокальцитонина более 0,5 нг/мл, появление гнойной мокроты, лейкоцитоз более 12×109/л (в отсутствие предшествовавшего применения глюкокортикоидов), повышение числа палочкоядерных нейтрофилов более 10%). Такие ситуации встречаются в амбулаторных условиях не более чем в 2–7% случаев [1, 2, 6].
Несмотря на вышесказанное, АБС все же довольно активно назначались в изученных амбулаторных случаях, особенно до осени 2020 г., что частично можно объяснить отсутствием четкой позиции в различных кругах медицинского сообщества по применению АБС. Так, азитромицин присутствовал в качестве возможного этиотропного препарата вплоть до 9-й версии временных методических рекомендаций, изданных 26.10.2020 [12–14], хотя к тому времени в мире уже были получены убедительные данные касательно нерационального применения АБС при новой коронавирусной инфекции. В нашем исследовании первый курс АБС в группе COVID-19 (-) имел место в 34,1% случаев со следующим распределением ЛС: левофлоксацин и азитромицин (33,3 и 26,7% соответственно), цефтриаксон – 23,3%, амоксициллин+клавулановая кислота – 13,3% и амоксициллин – 3,3%.
В группе COVID-19 (+) АБС назначались «на старте» в 27,5% случаев и наиболее применяемым препаратом был азитромицин – 50%, также применялись цефтриаксон и левофлоксацин (по 20%), цефдиторен (Спектрацеф) и амоксициллин с клавулановой кислотой (оба в 5% случаев).
Второй курс АБС, либо первичное назначение АБС на повторном приеме, в группе COVID-19 (+) отмечался значимо реже – в 5,8% случаев и был представлен азитромицином (4 эпизода из 69 случаев лечения). В группе COVID-19 (-) в 82 случаях терапии второй курс приема АБС был назначен также 4 (4,9%) раза, из которых азитромицин применялся 2 (2,4%) раза, левофлоксацин и цефетриаксон по 1 разу. Кроме того, в данной группе однажды был назначен третий курс АБС (левофлоксацин – 1,2%). Общее количество назначений АБС в группе COVID-19 (+) на один эпизод лечения составило 0,35, в группе COVID-19 (-) – 0,43.
Антикоагулятная терапия в амбулаторных условиях показана пациентам со среднетяжелой формой COVID-19 и высоким риском венозных тромбоэмболических осложнений при низком риске кровотечений. Препаратами выбора при этом являются низкомолекулярный гепарин и пероральные антикоагулянты (ривароксабан, апиксабан или дабигатрана этексилат). Как было указано, антикоагулянты в назначениях специалистов встречались достаточно редко. Частота назначений антикоагулятных препаратов в группе «COVID-19 (-) составила 7,3% (k=0,073); ЛС были представлены апиксабаном, ривароксабаном и дабигатраном (по 16,7%), чаще назначался антиагрегант дипиридамол (50% назначений в данной группе). В группе COVID-19 (+) препараты этой группы были назначены в 13% случаев (k=0,13) и представлены апиксабаном (22,2%), ривароксабаном (44,4%) и антиагрегантами в равной доле (ацетилсалициловая кислота, клопидогрел и дипиридамол в 11,1% случаев каждый).
В качестве патогенетического лечения на амбулаторном этапе, согласно актуальным временным методическим рекомендациям, может быть использован ингаляционный будесонид [1]. По данным некоторых исследований, данный препарат помогает снижать потребность пациентов с COVID-19 в неотложной медицинской помощи, а также сокращать время восстановления после перенесенной инфекции [7–9]. В проанализированных нами амбулаторных картах ингаляционный будесонид не встречается (отметим, что на момент проведения исследования данное ЛС не входило в рекомендации). Врачи отдавали предпочтение назначению пероральных и парентеральных форм глюкокортикостероидов (дексаметазон, метилпреднизолон): в группе COVID-19 (+) данные препараты назначались в 14,5% случаев (k=0,16), группе COVID-19 (-) они не назначались.
Среди всех витаминов аскорбиновая кислота (витамин С) занимает твердую лидирующую позицию по частоте назначений: в группе COVID-19 (+) – 78,7% и в COVID-19 (-) – 68,6%, что традиционно объясняется специалистами, применяющими его в подобных ситуациях, антиоксидантным действием, способностью поглощать свободные радикалы, иммунокоректирующей активностью, однако доказательная база таковых рекомендаций достаточно слабая [10].
В качестве симптоматических средств рекомендуются к использованию жаропонижающие препараты, назальные деконгестанты, мукоактивные и бронхолитические препараты.
Муколитики и противокашлевые средства были назначены в 41,5% эпизодов лечения (k=0,57) в группе COVID-19 (-). Эти ЛС были представлены ацетилцистеином и амброксолом (в 23,4% случаев каждый), бромгексином и бутамиратом (по 17%), антителами к брадикинину, гистамину и морфину аффинно очищенными (Ренгалин, 8,5%), комбинацией бромгексина–гвайфенезина–сальбутамола (Аскорил, 4,3%), карбоцистеином, экстрактом алтея (Мукалтин) и сиропом Гербион (без уточнения разновидности) – все по 2,1% случаев.
В группе COVID-19 (+) мукоактивные и противокашлевые ЛС назначены в 23,2% эпизодов (k=0,29). При этом частота назначения бромгексина составила 40% от всех назначений группы, ацетилцистеина – 25%, амброксола – 15%, комбинации бромгексина–гвайфенезина–сальбутамола – 10%, экстракта алтея и бутамирата – по 5%. Условно объединенная нами группа препаратов «Прочие ЛС» включает достаточно большое количество неродственных лекарственных средств, использованных специалистами для лечения ОРВИ/ COVID-19. В группе COVID-19 (-) они применялись в 69,5% случаев (k=1,32), в группе COVID-19 (+) – в 47,8% (k=0,72).
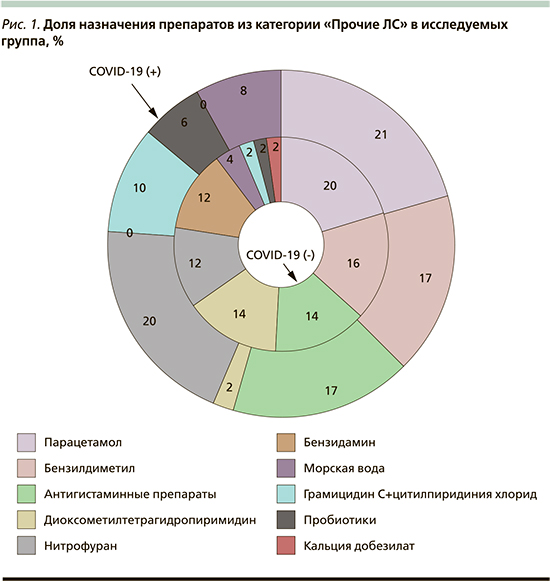
Для удобства восприятия ЛС представлены на диаграмме, отражающей случаи назначений данных препаратов в обеих группах (рис. 1).
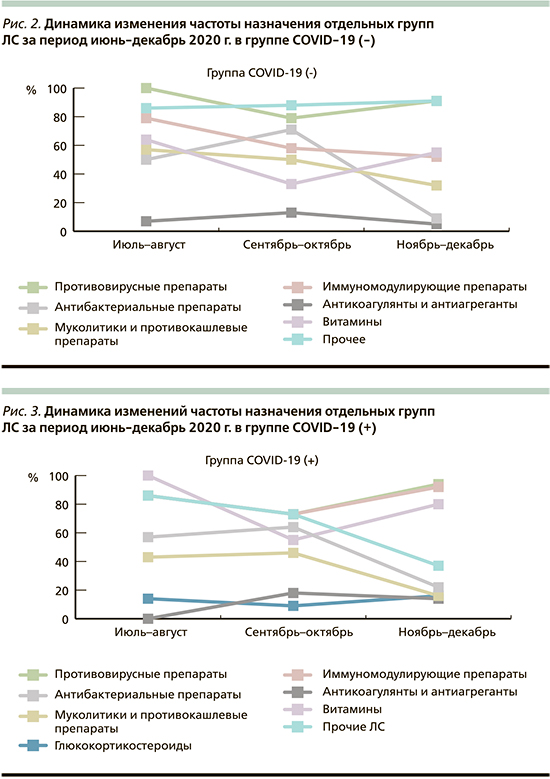
Динамика изменений частоты назначений представленных групп за период с июня по декабрь представлена на рис. 2, 3.
Обсуждение
Авторами проанализирована общая динамика назначений по всем группам ЛС. С июня по декабрь 2020 г. в группе «COVID-19 (-) наблюдалось неравномерное значимое снижение частоты назначения АБС – с 63,2 до 9,1% (p<0,05, z=6,04). Одним из факторов, влиявших на такую динамику, авторы могут считать проведение в ЛПУ мероприятий, направленных на рациональное использование АБС, которые стали активно проводится с сентября–октябрь 2020 г. [11]. Отмечено незначительное снижение частоты назначений противовирусных средств со 100 до 90,9%, средств группы «Прочие ЛС» с 85,7 до 54,5%, иммуномодуляторов с 78,6 до 52,3%, витаминов с 64,3 до 54,5%, антикоагулянтов и антиагрегантов с 7,1 до 4,5%; назначение муколитиков и противокашлевых препаратов к декабрю снизилось с 57,1 до 31,8%.
В группе COVID-19 (+) в период с июня по декабрь 2020 г. наблюдалось значимое снижение частоты назначения АБС – с 85,7 до 21,6% (p<0,05, z=3,43). Также снижалась частота назначений группы «Прочие ЛС» с 85,7 до 37,3%, витаминов со 100 до 80,4%, муколитиков и противокашлевых средств с 42,9% до 15,7%; отмечался рост назначений иммуномодулирующих средств с 85,7 до 92,2%, противовирусных препаратов с 85,7 до 94,1%, глюкокортикостероидов с 14,3 до 15,7%, а также антикоагулянтов и антиагрегантов с 0 до 13,7%.
Заключение
В ходе анализа результатов проведенного исследования нами был сделан вывод: на момент опроса врачи амбулаторного звена не имели достаточно четкого представления о текущих рациональных подходах к лечению новой коронавирусной инфекции. Однако в динамике с июня по декабрь 2020 г., в т. ч. на фоне проведения в ЛПУ образовательных мероприятий, ряд параметров терапии значимо улучшился – так, уровень избыточного применения антимикробных препаратов существенно снизился. Авторы приходят к выводам, согласно которым рационально регулярное проведение дополнительных образовательных и информационных мероприятий в амбулаторном терапевтическом звене ЛПУ, внедрение алгоритмов помощи врачам, программ поддержки принятия решений [11], которые позволяют улучшать знания специалистов в данном вопросе и повышать качество проводимой фармакотерапии.



