Введение
С развитием новых технологий, позволяющих наиболее эффективно доставлять экзогенный инсулин в организм, значительно расширились возможности лечения сахарного диабета (СД) [1]. Более 35 лет непрерывное подкожное введение инсулина (НПВИ), также известное, как помповая инсулинотерапия (ПИ), активно применяется в качестве лечения пациентов с СД [2]. Раньше данный вид лечения применялся преимущественно в отношении пациентов с СД 1 типа (СД1) как наиболее эффективный. Однако недавно проведенные клинические исследования по оценке эффективности ПИ у пациентов с СД2 также показали клинически значимые улучшения показателей углеводного обмена у пациентов этой группы [3]. За последние десятилетия ПИ не только улучшилась в техническом плане, но и стала более доступной [4]. Так, в России в 2015 г. более 15 тыс. пациентов использовали этот метод лечения СД [5]. При этом относительно высокая цена подобных устройств компенсируется улучшением не только углеводного обмена [4, 6], но и качества жизни [7].
Новые возможности сахароснижающей терапии
Одной из приоритетных задач при подборе инсулинотерапии является достижение адекватного гликемического контроля, которого можно добиться в т.ч. путем снижения выраженности постпрандиальной экскурсии глюкозы крови [8]. При этом очевидно, что чем лучше экзогенный инсулин имитирует физиологическую секрецию, тем лучше удастся достичь намеченных целей. Так, на смену ранее существовавшим растворимым человеческим инсулинам пришли аналоги человеческого инсулина (Лизпро, Аспарт, Глулизин) [9–11], которые эффективнее снижали постпрандиальную экскурсию глюкозы [12]. Однако, несмотря на это преимущество, в ряде исследований [8, 13, 14] показано, что для достижения целевых показателей постпрандиальной гликемии инъекцию необходимо осуществлять за 15–20 минут до приема пищи.
Этот факт не позволяет достигать желаемого удобства использования инсулина в ритме повседневной жизни [8]. Хотя всасывание из места инъекции аналогов человеческого инсулина происходит быстрее, чем растворимых человеческих инсулинов, этого все еще недостаточно, чтобы достигать адекватного подавления печеночного глюконеогенеза и оптимальных показателей постпрандиальной гликемии [15]. При этом постпрандиальные повышения уровня глюкозы крови >10 ммоль/л остаются частым явлением у пациентов, находящихся не только на базис-болюсной инсулинотерапии [8, 13], но и на ПИ [16], и использующих системы закрытого контура (closed-loop systems) [17–19].
Необходимость в разработке инсулина, который бы действовал еще быстрее, чем уже существующие аналоги, и как следствие – лучше бы имитировал секрецию эндогенного инсулина, привела к разработке инсулина аспарт сверхбыстрого действия (Фиасп®, Novo Nordisk A/S, Denmark) [20]. Его отличительной особенностью является добавление никотинамида (витамин В3) и L-аргинина, что ускоряет его всасывание из депо, а в результате позволяет быстрее достичь сахароснижающего эффекта. L-аргинин выступает в качестве стабилизатора, в то время как никотинамид ускоряет всасывание из подкожно-жировой клетчатки [21]. Безопасность и эффективность инсулина Фиасп® доказана в ряде рандомизированных клинических исследований (РКИ) в отношении пациентов, находящихся как на базис-болисной инсулинотерапии [22, 23], так и на ПИ [24]. Сравнение проводилось между классическим инсулином аспарт и Фиасп®. При этом оба исследуемых вида инсулина одинаково снижали уровень гликированного гемоглобина (HbA1c) и не различались по числу возникновения гипогликемических реакций. Более того, в группе пациентов, получавших Фиасп, снижение уровня глюкозы крови через 30, 60 и 120 минут после теста со стандартной пищевой нагрузкой было статистически более выражено, чем у инсулина аспарт [20] (рис. 1).
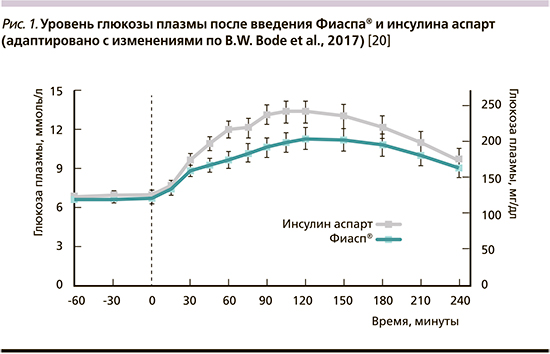
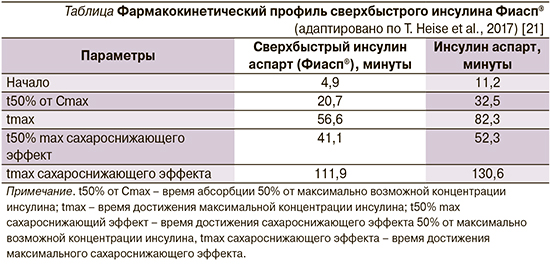
Отличие фармакокинетических свойств инсулина Фиасп® от инсулина аспарт наиболее выражено в скорости его абсорбции и распределения. Его фармакокинетический профиль у пациентов на ПИ был изучен и наглядно продемонстрирован в исследовании T. Heise et al. (см. таблицу) [21].
Применение инсулина Фиасп® у пациентов особых групп
Отметим, что исследования, проведенные среди групп пациентов на разных стадиях почечной и печеночной недостаточности, не показали различий в фармакокинетических свойствах сверхбыстрого инсулина аспарт по сравнению с другими инсулинами. Тем не менее производитель отмечает, что в данной группе пациентов по аналогии с применением других видов инсулина могут потребоваться коррекция дозы и частый контроль уровня глюкозы крови [25].
В ряде исследований [22, 23] в группу включали пожилых пациентов в возрасте до 75 лет. При этом не было выявлено различий в эффективности и безопасности инсулина Фиасп® по сравнению с инсулином аспарт.
При сравнительном исследовании различных возрастных групп (дети в возрасте 6–11 лет; подростки в возрасте 12–17 лет и взрослые в возрасте 18–64 лет) были выявлены статистически значимые различия во времени начала действия инсулина Фиасп®. Было показано, что время начала действия сверхбыстрого инсулина, а также его сахароснижающий эффект были более выражены у детей и подростков. Тем не менее эффективность и безопасность инсулина Фиасп® были сопоставимыми в исследуемых группах [26].
Опыт применения сверхбыстрого инсулина аспарт (Фиасп®) в отечественной практике
До 2015 г. внедрение ПИ и систем непрерывного мониторинга гликемии (НМГ) в отечественную клиническую практику проходило достаточно медленно. С внедрением программы высокотехнологичной медицинской помощи (ВМП) в систему обязательного медицинского страхования (ОМС) число пациентов, переведенных на ПИ, резко возросло. Так, в отделении терапевтической эндокринологии ГБУЗ МО МОНИКИ в 2015–2020 гг. помпы были установлены более 1000 больным СД.
В 2019 г. новый сверхбыстрый инсулин аспарт (Фиасп®) получил регистрационную лицензию на применение в Российской Федерации. Ввиду его очевидных фармакокинетических преимуществ перед ультракороткими инсулинами [20, 21, 24] в отделении терапевтической эндокринологии ГБУЗ МО МОНИКИ им М.Ф. Владимирского начато его применение пациентами на ПИ.
Клинический случай
Пациентка Татьяна А. 27 лет поступила в отделение терапевтической эндокринологии ГБУЗ МО МОНИКИ им. М.Ф. Владимирского 01.02.2021 для установки инсулиновой помпы в рамках оказания высокотехнологичной медицинской помощи (ВМП, раздел 1).
Жалобы при поступлении на периодическую сухость во рту, ощущение покалывания в пальцах стоп, общую слабость.
Анамнез заболевания: СД1 с 13-летнего возраста (в течение 14 лет), стойкой компенсации заболевания не было, со слов, никогда.
Гликемия от 3,0 до 20,0 ммоль/л в течение суток, тяжелые гипогликемические реакции отрицает, легкие гипогликемии 1–2 раза в месяц, кетоацидотическая кома в 2017 г. Основными знаниями о СД обладает: подсчет углеводов по системе «хлебных единиц» (ХЕ), правила профилактики и купирования гипогликемии и другие необходимые базовые знания.
Исходная терапия на момент поступления: инсулин Детемир 18 ЕД 2 раза в сутки (утром и в 22.00)+инсулин аспарт 3–4 раза в сутки, исходя из потребности 1.5 ЕД на 1 ХЕ в завтрак и ужин и 2 ЕД на 1 ХЕ в обед. Самоконтроль: гликемия по глюкометру 3–5 раз в сутки.
Анамнез жизни и семейный анамнез: без особенностей.
Физикальное обследование: индекс массы тела – 24,8 кг/м2, артериальноедавление – 120/80 мм рт.ст., частота сердечных сокращений – 78 в минуту, стул, диурез в норме. Болевая чувствительность в области стоп снижена, тактильная и температурная сохранены.
В местах инъекций инсулина множественные участки липогипертрофий.
В остальном без особенностей.
Ключевые особенности случая: основная проблема – выраженные колебания гликемии в течение суток (от 3,0 до 20,0 ммоль/л). Особенностью также оказалась боязнь гипогликемических реакций, отсутствие у пациентки веры в возможность принципиального улучшения ситуации.
Результаты лабораторного и инструментального обследования: HbA1c – 13,2%, скорость клубочковой фильтрации (CKD-EPI) – 119,9 мл/мин/1,73 м2, суточная протеинурия – 1,03 г (0,02–1,141), дислипидемия: липопротеиды низкой плотности – 4,6 ммоль/л (менее 1,8 ммоль/л); в остальном без клинически значимых изменений.
Пациентка осмотрена неврологом (установлен диагноз диабетической полиневропатии, дистальный тип, сенсорная форма) и офтальмологом (данных за диабетическую ретинопатию не получено).
На основании полученных данных сформулирован клинический диагноз: основной – СД1 (целевой уровень HbA1c менее 6,5%); осложнения: диабетическая нефропатия, хроническая болезнь почек С1А2, диабетическая полиневропатия, дистальный тип, сенсорная форма; сопутствующий: дислипидемия.
Лечение: 02.02.2021 пациентке установлена инсулиновая помпа Акку-Чек Комбо (Рош) и начата инсулинотерапия инсулином Фиасп в базальном режиме со скоростью 1,0 ЕД/ч (24 ЕД/сут.)+болюсное введение из рассчета 1,5 ЕД на 1 ХЕ в завтрак и ужин и 2 ЕД на 1 ХЕ в обед, коэффициент чувствительности к инсулину (КЧИ) – 3. Кроме того, начиная с 01.02.2021 пациентке проводилось флэш-мониторирование уровня глюкозы системой Фристайл Либра (Эбботт).
Данные флэш-мониторинга в условиях стационара представлены на рис. 2 и 3.
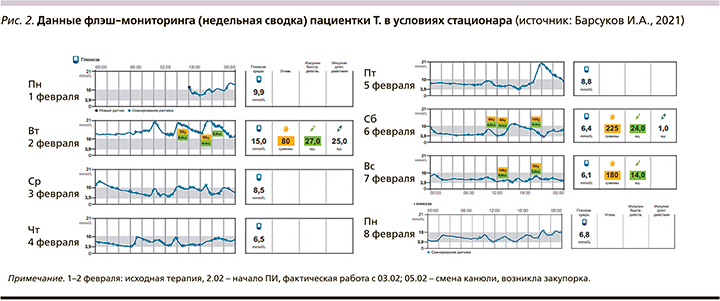
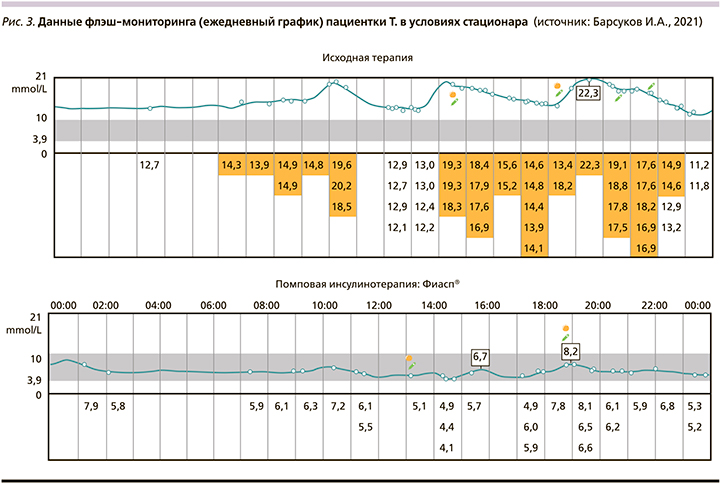
Из представленных на рис. 2 и 3 суточных графиков уровня глюкозы крови видно, что уже в условиях стационара достигнуты целевые уровни гликемии и, что очень важно, не наблюдается эпизодов гипогликемии и выраженных гипергликемических постпрандиальных пиков. Имел место однократный пик гликемии 05.02.2021 вечером, что было связано с эпизодом закупорки канюли инфузионной системы инсулиновой помпы, после устранения которой ситуация была нормализована.
После первичного обучения пациентки и фактического достижения целевых параметров углеводного обмена ее выписали из стационара, и далее флэш-мониторинг проводился уже в амбулаторных, «домашних», условиях. Данные мониторинга в амбулаторных условиях представлены на рис. 4 и 5.
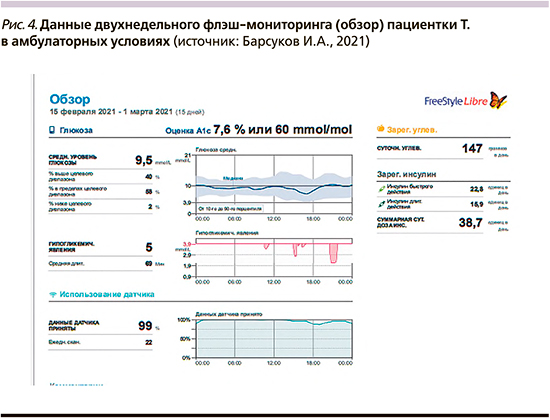
Как видно из представленных графиков, расчетный уровень HbA1c составил 7,6%, что позволяет говорить о хорошем прогрессе в терапии (при поступлении в стационар был 13,2%). Время в целевом диапазоне 3,9–10,0 ммоль/л («Time in Range», TIR) составило 58%, что несколько ниже целевого параметра, который, как правило, определяется в 70% [27]. При этом время в диапазоне ниже целевого составило 2%, что является допустимым показателем. Тем не менее у пациентки однократно зарегистрирован эпизод гипогликемической реакции с уровнем гликемии менее 3,0 ммоль/л, что требует тщательного анализа и устранения предпосылок для возникновения подобных эпизодов в дальнейшем.
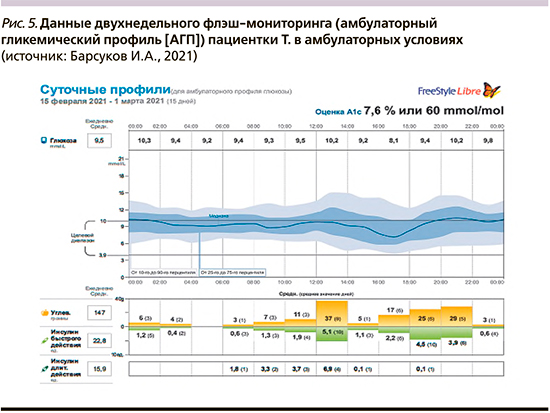
Достигнутый прогресс в компенсации диабета при продолжении работы с данной пациенткой и сохранении ее высокой мотивации, несомненно, приведет к достижению целевых параметров гликемии и HbA1c уже в краткосрочной перспективе 3–5 месяцев.
Обсуждение
Процесс подбора различных режимов введения инсулина с помощью инсулиновой помпы не ограничивается начальной настройкой прибора в стационаре. Это достаточно длительный процесс, осуществляемый в основном пациентом самостоятельно с минимальным направляющим участием врача-эндокринолога. Как правило, требуется от нескольких недель до нескольких месяцев, чтобы персонифицировать инсулинотерапию с помощью помпы. Максимально быстродействующие препараты инсулина, особенно новый препарат сверхбыстродейтсвующего инсулина аспарт (Фиасп), позволяют сократить и упростить этот процесс, значительно повышая качество жизни пациентов с СД.
Заключение
С учетом фармакокинетических особенностей сверхбыстрого инсулина представляется логичным его применение в помповой инсулинотерапии для достижения лучших результатов в управлении гликемией.


