Введение
Радикальная цистэктомия (РЦЭ) остается основным методом лечения пациентов с неметастатическим мышечно-инвазивным раком мочевого пузыря (МИРМП) и немышечно-инвазивным раком мочевого пузыря (НМИРМП) высокой степени злокачественности [1, 2].
Травматичность и техническая сложность данного оперативного вмешательства, а также пожилой возраст пациентов и их отягощенный коморбидный статус обусловливают высокую частоту ранних и поздних послеоперационных осложнений и летальности после РЦЭ [3, 4].
Один из путей снижения морбидности РЭЦ – снижение травматичности хирургического доступа, что возможно при использовании малоинвазивных технологий, таких как лапароскопическая и робот-ассистированная хирургия. С учетом существенной технической сложности цистэктомии (ЦЭ) и деривации мочи при лапароскопической технике применение робот-ассистированной цистэктомии (РАЦЭ) представляется наиболее перспективным методом лечения таких пациен-тов [5].
РАЦЭ впервые выполнена M. Menon [6], a W.D. Beecken были опубликованы результаты первой РАЦЭ c интракорпоральным формированием мочевого резервуара [7]. С того времени начинается ее активное распространение по всему миру. К настоящему времени накоплен значительный опыт выполнения таких оперативных вмешательств, который продемонстрировал, что их онкологические результаты не уступают открытой хирургии, при этом снижаются сроки реабилитации пациентов и сохраняется высокое качество их жизни [8, 9]. Тем не менее продолжается дискуссия о выборе наиболее оптимальной хирургической техники РЦЭ и формирования илеокондуита или необладдера [8, 9].
Цель исследования: анализ ближайших и отдаленных результатов РАЦЭ с применением различных способов деривации мочи пациентов с уротелиальной карциномой мочевого пузыря (МП).
Методы
В настоящее исследование были включены 16 пациентов, 15 (93,8%) мужчин и 1 (6,2%) женщина с РМП, которым в период с 2020 по 2023 г. в отделении хирургических методов лечения урологических заболеваний ФГБУ НМИЦ хирургии им А.В. Вишневского Минздрава РФ выполнена РАЦЭ с различными видами деривации мочи. Распределение операций (общее и по методу деривации мочи) по годам представлено на рис. 1.
В зависимости от метода деривации мочи все пациенты были разделены на 3 группы (рис. 2): I (n=7, 43,7%) – формирование ортотопического мочевого резервуара по Штудеру, II (n=5, 31,3%) – создание илеокондуита по Бриккеру, III (n=4, 25,0%) – двусторонняя уретерокутанеостомия (УКС).
Выбор метода деривации мочи определялся оперирующим хирургом и зависел распространенности опухоли, возраста пациента, его сопутствующей патлогии и функционального состояния.
Средний возраст пациентов составил 64,6±9,0 лет (40–75 лет). Распределение пациентов по возрастным группам представлено на рис. 3.
Средний индекс коморбидности Charlson – 5±1 (3–8). ECOG-0 – у 10, ECOG-1 – у 6 пациентов. Среднее число баллов по шкале ASA – 3 (2–3). Средний индекс массы тела (ИМТ) – 26,0±8,1 кг/м2 (20,0–47,0 кг/м2).
У одного из пациентов до начала лечения имела место вторая синхронная опухоль – рак предстательной железы (ПЖ) T3bN0M0G3, по поводу которой проводилась гормональная терапия.
Всем пациентам проведено обследование в соответствии с Национальными клиническими рекомендациями [10].
Критерии включения: верифицированная уротелиальная карцинома МП, наличие показаний к ЦЭ, функциональное состояние, позволяющее выполнять ему радикальную операцию, согласие пациента на ЦЭ с одним из видов деривации мочи, способ которого обсуждался с пациентом перед операцией.
Критерии невключения: наличие декомперсированной сопутствующей патологии, выраженный спаечный процесс после предшествующих хирургических вмешательств на органах брюшной полости, заболевания кишечника, препятствующие его использованию для формирования илеокондуита или мочевого резервуара, отказ пациента от органоуносящей операции.
Критерии исключения: отказ пациента от последующего за ним динамического наблюдения после выписки.
Клинические особенности пациентов представлены в табл. 1.
Техника операции. Оперативное вмешательство проводилось с использованием роботической системы Da Vinci Si (Intuitive Surgical, США). Пациента укладывали в положение лежа на спине со слегка опущенным ногами и валиком под крестцом (положение Тренделенбурга 25–30 градусов). После введения пациента в наркоз, внутривенной инфузии профилактической дозы антибиотика (цефалоспорин 2–3-го поколений), трехкратной обработки растворами антисептиков операционного поля и его отграничения стерильным хирургическим бельем, выполнялся разрез кожи по средней линии живота на 1 см выше пупка. Через данный разрез по стандартной методике осуществлялась пункция брюшной полости иглой Вереша для создания пневмоперитонеума. После достижения давления в брюшной полости 10–12 мм рт.ст. производилась установка 12 мм порта для камеры 0º. После ее введения проводилась ревизия брюшной полости, после чего под контролем камеры выполнялась установка других портов. Два 10 мм порта устанавливались на уровне пупка по латеральному краю прямых мышц живота на расстоянии около 5 см от камеры. Третий роботический 10 мм-порт располагался на 1 см выше и кнутри от передней верхней ости правой подвздошной кости. Ассистентский 12 мм-порт устанавливался слева, зеркально третьему порту. Второй ассистентский 5 мм-порт устанавливался слева на 1 см к внутри от середины расстояния между камерой и левой роботической рукой.
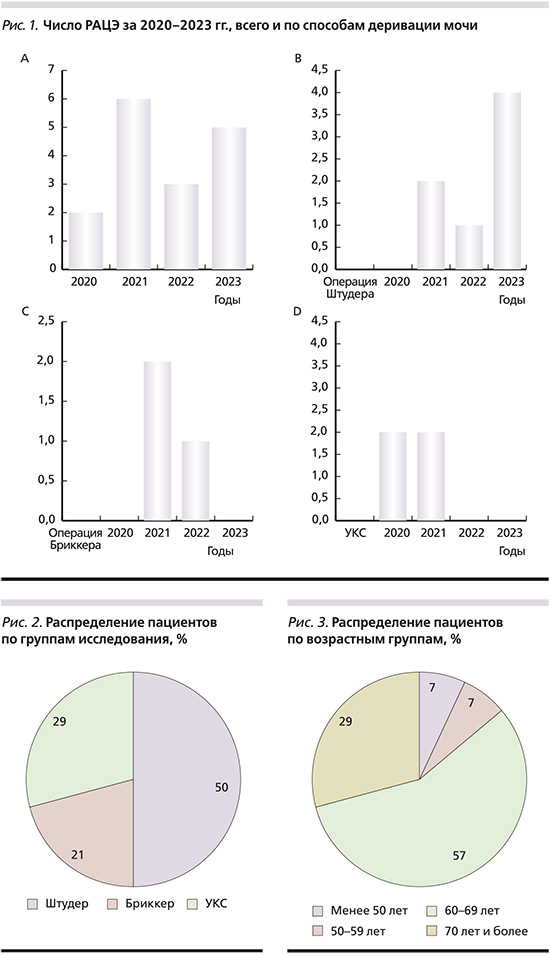
После установки портов и докинга робота первым этапом операции выполнялась лимфаденэктомия, для чего с помощью биполярной коагуляции с обеих сторон удалялась жировая клетчатка с лимфоузлами между наружной и внутренней подвздошными артериями до их бифуркации, а также из обтураторной ямки с выделением запирательных нерва и артерии (рис. 4).
Далее производилась мобилизация мочеточников, которые поэтапно выделялись от зоны перекреста с подвздошными сосудами до юкставезикального отдела, где на них накладывались по две клипсы, между которыми мочеточники пересекались. Левый мочеточник проводился в правую подвздошную области через окно, сформированное в брыжейке сигмовидной кишки под нижней брыжеечной артерией.
Следующим этапом выполнялась мобилизация МП и ПЖ. При помощи монополярной коагуляции параллельно пупочным связкам вскрывали париетальную брюшину. После пересечения пупочной связки осуществляли вход в предпузырное пространство. Далее выделяли МП и переднюю поверхность ПЖ. Тазовую фасцию вскрывали латеральнее ПЖ. Пересекали лобково-простатические связки. Дорзальный венозный комплекс перед пересечением лигировали непрерывным обвивным викриловым швом (3/0). После пересекали уретру, ПЖ отделяли от передней стенки прямой кишки, рассекали фасцию Денонвилье–Салищева и выделяли семенные пузырьки. Семявыносящие протоки пересекали с использованием биполярной коагуляции. Лигировали пузырные сосуды. МП, мобилизованный единым блоком с ПЖ, удаляли через расширенный разрез в месте установки камеры.
Во всех случаях оперативное вмешательство осуществлялось без использования нервосберегающей методики для достижения его максимальной радикальности.
Следующим этапом операции осуществляли деривацию мочи.
Двусторонняя УКС. Мочеточники интубировали J-образными мочеточниковыми стентами и через сформированные каналы выводили на кожу в обеих подвздошных областях, где фиксировали к коже без натяжения четырьмя узловыми швами. После формирования уретерокутанеостом дистальный конец мочеточников выступал над поверхностью кожи не менее чем на 2 см.
Конверсий к открытой операции не было.
Формирование илеокондуита по Бриккеру. На расстоянии 25 см от илеоцекального угла выделяли сегмент подвздошной кишки длиной 25–30 см.
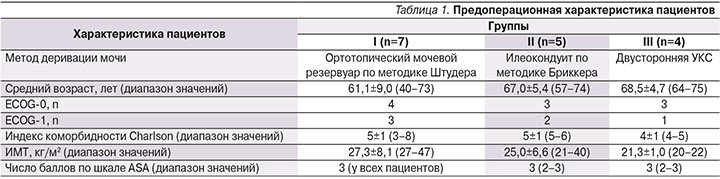
Кишку пересекали с помощью линейного сшивающего аппарата. Накладывали аппаратный (Endo Gia 45 мм (4)+60 мм (1)) латеролатеральный энтероэнтероанастомоз (рис. 5).
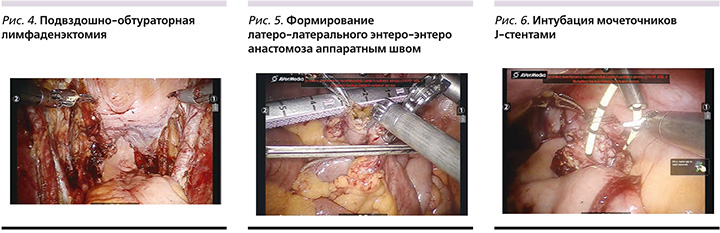
Спатулированные мочеточники сшивали между собой по методике Wallace 1. Изолированный сегмент подвздошной кишки выводили через разрез в правой подвздошной области, где формировалась уростома. Через ассистентский порт в брюшную полость вводили мочеточниковые J-стенты. Проводили интубацию мочеточников (рис. 6). Используя зажим Шамли, стенты выводили наружу через уростому, после чего с помощью непрерывного шва (Монокрил 5/0) формировали уретероилеоанастомоз.
В одном случае в связи с техническими сложностями, обусловленными анатомическими особенностями пациента, на этапе формирования энтеро-энтероанастомоза и илеум-кондуита была выполнена конверсия к открытой операции.
Формирование ортотопического мочевого резервуара по методике Штудера. На расстоянии 25 см от илеоцекального перехода выделяли сегмент подвздошной кишки длиной 55 см. Кишку пересекали с помощью линейного сшивающего аппарата. Проходимость тонкой кишки восстанавливали аппаратным (Endo Gia 45 мм (4)+60 мм (1)) латеролатеральным анастомозом. Дистальные 40 см отрезка кишки детубуляризировали, укладывали в виде буквы U и сшивали непрерывным однорядным швом (Викрил 3/0). Таким образом формировался необладдер.
Заднюю стенка резервуара складывали в поперечном направлении в соотношении 2/3 к 1/3. Продольную часть передней стенки необледера ушивали непрерывным викриловым (3/0) швом (рис. 7). В качестве технологического окна для манипуляций внутри необладдера оставляли неушитой 1/3 передней стенки. Дистальные части мочеточников пересекали ниже ранее наложенных клипс и направляли на патоморфологическое исследование. Затем мочеточники интубировали наружными J-стентами.

Интубированные мочеточники проводили в недетубуляризированную часть резервуара и фиксировали к нему монокриловыми (5/0) узловыми швами. В апикальной точке каудальной части необладдера выполняли контрапертуру диаметром 2–3 мм. Через нее проводили мочеточниковые стенты (рис. 8), которые выводили через уретру. Затем в необладдер устанавливали катетер Фоллея № 18 Ch.
Оставшуюся треть неушитого нео-бладдера герметично ушивали непрерывным швом (Викрил – 3/0). Далее ортотопический резервуар низводили в малый таз (рис. 9), после чего накладывали анастомоз (Монокрил – 5/0) между уретрой и шейкой необладдера.
В одном случае в связи с невозможностью ретроградного стентирования мочеточника (из-за стриктуры в его нижней трети) была произведена конверсия к открытой операции.
Результаты
Характеристики оперативного вмешательства в группах исследования представлены в табл. 2.

Как видно из данной таблицы, наибольшая длительность операции была в группе формирования необладдера (группа I), что объясняется ее большей технической сложностью. Наименьшая длительность оперативного вмешательства ожидаемо отмечена в группе УКС (группа III).
Наибольшая интраоперационная кровопотеря также отмечена в группе I, а наименьшая – в группе III.
Среднее число удаленных лимфоузлов было существенно больше в группе I.
Положительный хирургический край выявлен у 4 пациентов: 2 – из группы II и 2 – из группы III. У всех из них отмечены другие неблагоприятные морфологические характеристики опухоли: ее местное распространение, периневральный рост, венозная и лимфоваскулярная инвазия.
Показатели, характеризующие послеоперационное течение у пациентов в группах исследования, представлены в табл. 3.

Наибольшее число осложнений отмечено в группе I, что связано с большей технической сложностью оперативного вмешательства в отношнии пациентов данной группы.
Все осложнения отнесены к степени II–IIIa по шкале Clavien–Dindo и были успешно купированы в процессе лечения пациентов.
Табл. 4 демонстрирует результаты наблюдения за пациентами в отдаленном периоде. Наибольшая медиана наблюдения (32 месяца) – в группе III, поскольку УКС выполнялась на этапе освоения роботической ЦЭ.

Прогрессирование заболевания диагностировано у 2 пациентов из группы II. Все они, по данным патоморфологического исследования удаленного МП, имели неблагоприятные характеристики опухоли. Одному из этих пациентов была выполнена экстирпация уретры в связи с выявленными в ней имплантационными метастазами через 5 месяцев после операции. У другого пациента через 4 месяца после ЦЭ диагностированы метастазы в кости и начато лекарственное лечение в условиях отделения химиотерапии нашего учреждения. Этот пациент умер от прогрессирования онкокологического заболевания через 1,5 года после операции.
Обсуждение
Развитие современных медицинских технологий оказало значимое влияние на хирургическую тактику лечения многих заболеваний, в т.ч. рака МП [11]. Робот-ассистированные операции считаются альтернативой открытой хирургии, т.к. они обеспечивают минимальную травматичность хирургического доступа и высокую прецизионность основного этапа операции, что сопровождается низкой частотой периоперационных осложнений и хорошими онкологическими результатами [12].
Ранее нами был проанализирован опыт роботических резекций МП [13], а в дальнейшем – ЦЭ [14]. Полученные нами результаты оказались обнадеживающими для продолжения дальнейших исследований в этом направлении. Частота послеоперационных осложнений составила 36%, что значимо ниже, чем у пациентов после открытой РЦЭ. По данным M. Hirobe et al., общая частота осложнений в течение 90 дней после операции составила 80,5%, ≥III степени по шкале Dindo–Clavien cоставила в исследуемой когорте 22,2% [4].
C.U. Lee уе фд. сообщили о частоте послеоперационных осложнений после РАЦЭ 61,9%, большинство из них (42,1%) – II степени по Clavien-Dindo [15]. B.H. Bochner et al. опубликовали данные о послеоперационных осложнениях II–IV степеней по Clavien–Dindo, которые были зарегистрированы у 66% пациентов в группе открытой РЦЭ и 62% – в группе РАЦЭ [9]. Эти цифры объясняются тем, что В.Н. Bochner et al. провели исследование в начале освоения методики РАЦЭ, в то время как, по данным Рабочей группы по роботической хирургии Европейской ассоциации урологов, выяснено, что выход на плато кривой обучения при проведении РАЦЭ требует выполнения не менее 97 таких операций [16].
При РАЦЭ отмечается минимальный объем кровопотери и, следовательно, низкая частота гемотрансфузий, что также подтверждается данными нашего исследования [17].
В нашем исследовании среднее время операции варьировалось в зависимости от способа деривации мочи. Наибольшее время ожидаемо потребовалось при формировании ортотопического резервуара, наименьшее – при выполнении УКС.
Полученные нами результаты согласуются с данными, опубликованными другими отечественными авторами [18–22].
Дальнейшее развитие хирургической техники РАЦЭ будет способствовать достижению лучших онкологических и функциональных ее результатов [23].
Заключение
РАЦЭ – перспективный метод хирургического лечения пациентов с МИРМП. В настоящее время в мире накоплен достаточно большой опыт выполнения данных оперативных вмешательств. Это позволило сделать убедительные выводы об их преимуществах перед открытой операцией. Несмотря на более высокую себестоимость роботической операции, в долгосрочной перспективе она может окупиться за счет снижения частоты осложнений, гемотрансфузий и сокращения сроков пребывания пациента в стационаре. Именно поэтому прослеживается стойкая тенденция к повышению доступности роботической хирургии в различных медицинских учреждениях, что также открывает возможности для дальнейших многоцентровых исследований в данной области, необходимых для оценки результатов РАЦЭ с интракорпоральным формированием ортотопического мочевого резервуара или илеокондуита, а также УКС.
Вклад авторов. А.А. Грицкевич – дизайн исследования, выполнение хирургических операций. В.А. Оганян – участие в операциях, анализ данных, написание текста. Д.М. Монаков – анализ данных, написание текста. А.Д. Симонов – анализ результатов, поиск публикаций по теме исследования. Н.А. Карельская – выполнение и анализ рентгеновских исследований. А.Г. Кочетов – поиск публикаций по теме исследования. Ж. Полотбек – участие в операциях, сбор данных. И.Г. Русаков – идея и организация исследования, научное консультирование.
Этическое одобрение. В связи с ретроспективным характером исследования одобрения локального этического комитета не требовалось.
Этическое заявление. Исследование выполнено в соответствии с положениями Хельсинкской декларации (Форталеза, Бразилия, октябрь 2013).
Информированное согласие. Все пациенты подписали информированное согласие на участие в исследовании и обработку персональных данных.



