Введение
В настоящее время во всех областях клинической медицины, в т.ч. в онкологии, увеличивается число коморбидных пациентов. Отчасти это связано с общей тенденцией к старению населения. Однако в большей степени это явление имеет место вследствие развития медицинских технологий, в частности, в связи со снижением токсичности проводимой лекарственной терапии, благодаря чему стало возможным проводить высокоэффективную противоопухолевую терапию коморбидным пациентам, которым раньше отказывали в патогенетическом лечении онкологического заболевания по причине высокого риска жизнеугрожающих побочных эффектов. Это в свою очередь сделало вопрос выбора схемы и режима дозирования противоопухолевой терапии в зависимости от сопутствующих заболеваний весьма актуальным. Наиболее значимы в этом отношении заболевания, влияющие на фармакодинамику и фармакокинетику лекарственных препаратов, а также вызывающие медикаментозно индуцированный иммунодефицит. Одним из фармакологически значимых ограничивающих факторов является нарушение функции почек, весьма распространенное среди пациентов онкологического профиля (до 50% случаев) [1–3].
По результатам наших исследований, проведенных на базе ГКБ им. Д.Д. Плетнева, 33% от общего числа пациентов, обратившихся за онкологической помощью, страдают также ХБП, что соответствует мировой статистике [1–3]. Среди пациентов, обследованных нами, наиболее часто нарушение фильтрационной функции почек имело место при почечно-клеточном раке (ПКР) – 21,21%. Несколько реже при злокачественных новообразованиях (ЗНО) предстательной железы и мочевого пузыря – 18,79 и 16,97% соответственно.
Согласно действующим Клини-ческим рекомендациям, для лечения ПКР в первой линии терапии целесообразно применять следующие схемы: пембролизумаб+ленватиниб, ниволумаб+кабозантиниб, пембролизумаб+акситиниб, ниволумаб+ипи-лимумаб [4]. Выбор схемы терапии во многом обусловлен прогнозом заболевания, который оценивается в т.ч. исходя из социальной адаптации пациента и способности его к самообслуживанию. Сопутствующие заболевания, в частности ХБП, несомненно, должны влиять на тактику медикаментозной терапии больных ПКР, однако в клинических рекомендациях пока нет однозначного руководства по тактике лечения таких пациентов: противо-опухолевая терапия формально разрешена при любой функции почек почек, поскольку для противоопухолевых препаратов, применяемых при ПКР, не характерна нефротоксичность [4, 5].
Крупных отечественных исследований, посвященных лечению ПКР в условиях ХБП, на данный момент нет. Информация из зарубежных источников ограниченна и посвящена преимущественно вопросам эпидемиологии, а также прогнозу лекарственной токсичности, исходя из предсуществующей фильтрационной функции почек [1, 2, 6, 7]. Информация по выбору оптимальной схемы лекарственной терапии и ее эффективности у таких пациентов весьма ограниченна и фрагментарна.
В частности, имеется описание успешного применения пембролизумаба при тяжелой ХБП (ХБП V ст.) [8].
Таким образом, исследование реальной клинической практики оказания онкологической помощи пациентам, страдающим ПКР на фоне ХБП, представляется весьма актуальным.
Методы
В данное ретроспективное исследование вошли 194 больных ПКР и ХБП, получавших лекарственную противоопухолевую терапию в ГКБ им. Д.Д. Плетнева в 2020–2022 гг.
Критерии включения: светлоклеточныйо почечно-клеточный рак (сПКР), подтвержденный при гистологическом исследовании; ХБП II–IV ст., терапия первой линии, включающая пембролизумаб и акситиниб. Лекарственная терапия назначалась по схеме: пембролизумаб 200 мг внутривенно капельно 1 раз в 3 недели, акситиниб, 5 мг 2 раза в сутки ежедневно перорально – до прогрессирования основного заболевания или развития побочных эффектов, делающих продолжение терапии невозможным.
Критерии невключения и исключения: применение других противоопухолевых препаратов, пембролизумаба и акситиниба в качестве второй линии терапии, непереносимость пембролизумаба или акситиниба, сопутствующая печеночная недостаточность любой степени выраженности, отказ пациента от участия в исследовании, добровольный отказ пациента от продолжения противоопухолевой терапии (по немедицинским причинам).
Пациенты были разделены на группы согласно прогностической модели IMDC и функциональному состоянию почек (табл. 1).
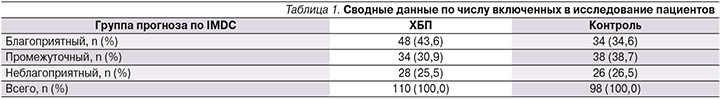
Контрольную группу составили сопоставимые по клинико-демографическим характеристикам пациенты с условно сохранной фильтрационной функцией почек, получающие противоопухолевую терапию по вышеуказанной схеме.
Все включенные в исследование пациенты (как основной, так и контрольных групп) находились под регулярным диспансерным наблюдением. Контрольные обследования проводились не реже чем 1 раз в 3 месяца. Информацию о состоянии пациентов, в т.ч. о фильтрационной функции почек, получали из медицинской документации. СКФ рассчитывали, исходя из текущего уровня креатинина по номограммам CKD-EPI. Эффективность терапии оценивалась по медиане ВБП и ОВ. Период наблюдения составил 24 месяца, что несколько превышает ВБП для комбинации пембролизумаба и акситиниба, назначенной в качестве первой линии терапии, рассчитанной в ходе многоцентрового исследования KEYNOTE-426 (15,1 месяца).
Статистическая обработка результатов проводилась с применением программ Microsoft Excel и Statistica 8.0 (StatSoftInc.).
Результаты
В подгруппах основной группы пациентов, выделенных, согласно прогнозу по IMDC, первым этапом было оценено распределение ХБП по стадиям (табл. 2).
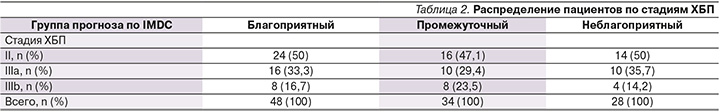
Во всех подгруппах основной группы преобладали пациенты со II (47,1–50,0%) и IIIa-стадиями ХБП (29,4–50%). Более тяжелый дефицит фильтрационной функции почек, соответствующий IIIb-стадии ХБП, встречался у единичных больных (14,2–23,5%), IV стадия ХБП не была отмечена ни у одного из пациентов, несмотря на то что она не являлась критерием невключения в исследование. Распределение по стадиям ХБП в анализируемых группах оказалось схожим, без статистически значимых различий.
Результаты терапии пациентов, страдающих ПКР на фоне ХБП, по вероятности полного или частичного ответа, а также по ОВ оказались сопоставимыми с контрольными группами (табл. 3).
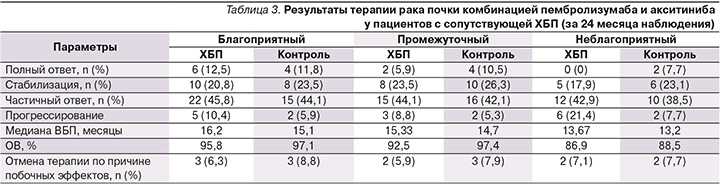
Негативное влияние ХБП прослеживается лишь у пациентов с неблагоприятным прогнозом, у которых частота прогрессирования ЗНО оказалась в 2,8 раза выше, чем у аналогичных пациентов с условно сохранной фильтрационной функцией почек (21,4 и 7,7% соответственно; p<0,05).
Также вполне ожидаемо в группах пациентов с неблагоприятным прогнозом медиана ВБП оказалась достоверно ниже, чем при благоприятном или промежуточном прогнозе (13,67, 16,2 и 15,33 месяца; p<0,05 – при ХБП; 13,2, 15,1 и 14,7 месяца; p<0,05 – при условно сохранной фильтрационной функции почек). Однако не было верифицировано значимого влияния функции почек на риск прогрессирования: различия по ВБП в группах пациентов, имеющих сопутствующую ХБП, по сравнению с группами контроля не достигли выбранного уровня достоверности (соответственно 16,2 и 15,1 месяца при благоприятном прогнозе, 15,33 и 14,7 при промежуточном прогнозе, 13,67 и 13,2 месяца при неблагоприятном прогнозе; p>0,05 во всех случаях).
Безопасность терапии определялась по частоте развития побочных эффектов, послуживших поводом для отмены выбранных препаратов. Такие явления имели место лишь у единичных пациентов без достоверного увеличения их вероятности при предсуществующем дефиците фильтрационной функции почек (соответственно 6,3 и 8,8% при благоприятном прогнозе, 5,9 и 7,9% при промежуточном прогнозе, 7,1 и 7,7% при неблагоприятном прогнозе; p>0,05 во всех случаях).
Обсуждение
Результаты лекарственной противоопухолевой терапии больных сПКР на фоне ХБП оказались неожиданно оптимистичными. Эффективность терапии, определявшаяся в нашем исследовании ВБП, в группах пациентов с ХБП была не ниже, чем при условно сохранной почечной функции. Отсюда следует, что дефицит фильтрационной функции почек (по крайней мере в отсутствие противопоказаний к противоопухолевой терапии умеренно выраженный – СКФ>30 мл/мин) не оказывает клинически значимого влияния на эффективность терапии ПКР.
Отсутствие негативного влияния ХБП на эффективность противоопухолевой терапии во многом определяется фармакокинетикой таргетных и биопрепаратов (преимущественно выводятся печенью) и сравнительно благоприятным профилем безопасности (относительно антиметаболитов и алкилирующих средств), что позволяет их назначать пациентам изучаемой категории длительно и в полной дозе. Именно невозможность назначения лекарственной терапии в эффективной дозе и на необходимый срок в конечном счете лежит в основе неудовлетворительных результатов лечения пациентов онкологического профиля с нарушением фильтрационной функции почек. Если эту проблему дозы и длительности/числа удается решить (или хотя бы существенно сгладить), эффективность, как правило, приближается к общепопуляционной, что мы и наблюдаем в данном исследовании. Как бы то ни было, ХБП всегда значимо негативно влияет на общее состояние пациента. Помимо онкоспецифической выживаемости ХБП влияет на ОВ, а также ассоциирована с риском вынужденной отмены противоопухолевой терапии.
Полученные результаты в целом соответствуют данным крупного исследования T. Funakoshi et al. (2018), в ходе которого отмечена соизмеримая с общепопуляционной ОВ пациентов онкологического профиля, имеющих также терминальную ХБП (V ст.) и получающих заместительную почечную терапию, при условии, что противоопухолевую терапию удалось провести [9]. Отметим, что эти пациенты по своему соматическому статусу существенно тяжелее по сравнению с включенными в настоящее исследование: в нашем исследовании преобладали пациенты с начальными проявлениями нарушения почечной функции (ХБП II–IIIa-стадий). Пациентов с более выраженным снижением функции почек (IIIb–IV стадии) были единицы.
В настоящее время под ХБП подразумевается «персистирующее в течение 3 и более месяцев поражение органа вследствие действия различных этиологических факторов, анатомической основой которого является процесс замещения нормальных анатомических структур фиброзом, приводящий к его дисфункции» [10]. Ранее под ХБП понималось «наличие любых маркеров, связанных с повреждением почек и персистирующих в течение более 3 месяцев вне зависимости от нозологического диагноза. В целом данным критериям так или иначе отвечают почти все пациенты, страдающие ПКР. Таким образом, подобный подход представляется формальным и не вполне отвечает запросам реальной онкологической практики, без необходимости усложняя понимание и без того весьма непростой клинической ситуации. Потому в настоящем исследовании выделялись пациенты со сниженной и условно сохранной фильтрационной функцией почек – без формирования группы с ХБП I ст.
Можно ли экстраполировать результаты применения комбинации пембролизумаба и акситиниба на другие схемы терапии сПКР, а также на другие гистологические формы ПКР? Как уже отмечалось, ХБП сама по себе не определяет эффективность терапии, но может воспрепятствовать ее проведению посредством повышения риска побочных эффектов, зачастую делающих лечение опаснее болезни. Если фармакокинетические и фармакодинамические характеристики, а также заявленный профиль безопасности альтернативных препаратов схожи с изученными в ходе настоящего исследования, то, на наш взгляд, результаты экстраполировать можно, однако подтверждение должно стать целью отдельного исследования. В целом при умеренно выраженной ХБП (II–III стадии) схемы таргетной и иммунотерапии можно назначать в отсутствие у них заявленной нефротоксичности.
Заключение
При ХБП (II–III стадии) терапия сПКР, включающая пембролизумаб и акситиниб, продемонстрировала сопоставимую эффективность и безопасность по сравнению с таковой у пациентов с условно сохранной функцией почек. Коррекции доз, кратности введения препаратов, длительности терапии при этом не требовалось.



